Abstract
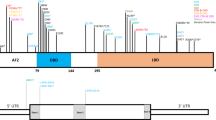
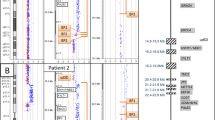
The introduction of array CGH in clinical diagnostics has led to the discovery of many new microdeletion/microduplication syndromes. Most of them are rare and often present with a variable range of clinical anomalies. In this study we report three patients with a de novo overlapping microdeletion of chromosome bands 12q15q21.1. The deletions are ∼2.5 Mb in size, with a 1.34-Mb common deleted region containing six RefSeq genes. All three patients present with learning disability or developmental delay, nasal speech and hypothyroidism. In this paper we will further elaborate on the genotype–phenotype correlation associated with this deletion and compare our patients with previously reported cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Menten B, Buysse K, Zahir F et al: Osteopoikilosis, short stature and mental retardation as key features of a new microdeletion syndrome on 12q14. J Med Genet 2007; 44: 264–268.
Schluth C, Gesny R, Borck G et al: New case of interstitial deletion 12(q15-q21.2) in a girl with facial dysmorphism and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet A 2008; 146A: 93–96.
Meinecke P, Meinecke R : Multiple malformation syndrome including cleft lip and palate and cardiac abnormalities due to an interstitial deletion of chromosome 12q. J Med Genet 1987; 24: 187.
Watson MS, McAllister-Barton L, Mahoney MJ, Breg WR : Deletion (12)(q15q21.2). J Med Genet 1989; 26: 343–344.
Perez Sanchez C, Ayensa F, Lloveras E et al: Prenatal diagnosis of an interstitial 12q chromosome deletion. Ann Genet 2004; 47: 177–179.
James PA, Oei P, Ng D, Kannu P, Aftimos S : Another case of interstitial del(12) involving the proposed cardio-facio-cutaneous candidate region. Am J Med Genet A 2005; 136: 12–16.
Tocyap ML, Azar N, Chen T, Wiggs J : Clinical and molecular characterization of a patient with an interstitial deletion of chromosome 12q15-q23 and peripheral corneal abnormalities. Am J Ophthalmol 2006; 141: 566–567.
Yamanishi T, Nishio J, Miya S et al: 12q interstitial deletion with bilateral cleft lip and palate: case report and literature review. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2008; 45: 325–328.
Vissers LE, Bhatt SS, Janssen IM et al: Rare pathogenic microdeletions and tandem duplications are microhomology-mediated and stimulated by local genomic architecture. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 3579–3593.
Collart MA : Global control of gene expression in yeast by the Ccr4-Not complex. Gene 2003; 313: 1–16.
Denis CL, Chen J : The CCR4-NOT complex plays diverse roles in mRNA metabolism. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 2003; 73: 221–250.
Abdelkhalek HB, Beckers A, Schuster-Gossler K et al: The mouse homeobox gene Not is required for caudal notochord development and affected by the truncate mutation. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 1725–1736.
Behrens R, Nolting A, Reimann F, Schwarz M, Waldschutz R, Pongs O : hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4, cloning and characterization of two members of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunit family. FEBS Lett 2000; 474: 99–106.
Brenner R, Jegla TJ, Wickenden A, Liu Y, Aldrich RW : Cloning and functional characterization of novel large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunits, hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 6453–6461.
Hunter T : Signaling--2000 and beyond. Cell 2000; 100: 113–127.
Zhang ZY : Protein tyrosine phosphatases: prospects for therapeutics. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2001; 5: 416–423.
Hendriks WJ, Dilaver G, Noordman YE, Kremer B, Fransen JA : PTPRR protein tyrosine phosphatase isoforms and locomotion of vesicles and mice. Cerebellum 2009; 8: 80–88.
Chirivi RG, Noordman YE, Van der Zee CE, Hendriks WJ : Altered MAP kinase phosphorylation and impaired motor coordination in PTPRR deficient mice. J Neurochem 2007; 101: 829–840.
Kuhn S, Koch M, Nubel T et al: A complex of EpCAM, claudin-7, CD44 variant isoforms, and tetraspanins promotes colorectal cancer progression. Mol Cancer Res 2007; 5: 553–567.
Scholz CJ, Jacob CP, Buttenschon HN et al: Functional variants of TSPAN8 are associated with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2010; 153B: 967–972.
Hsu SY, Liang SG, Hsueh AJ : Characterization of two LGR genes homologous to gonadotropin and thyrotropin receptors with extracellular leucine-rich repeats and a G protein-coupled, seven-transmembrane region. Mol Endocrinol 1998; 12: 1830–1845.
Hsu SY, Kudo M, Chen T et al: The three subfamilies of leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptors (LGR): identification of LGR6 and LGR7 and the signaling mechanism for LGR7. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 1257–1271.
Morita H, Mazerbourg S, Bouley DM et al: Neonatal lethality of LGR5 null mice is associated with ankyloglossia and gastrointestinal distension. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 9736–9743.
Curry CJ, Mao R, Aston E et al: Homozygous deletions of a copy number change detected by array CGH: a new cause for mental retardation? Am J Med Genet A 2008; 146A: 1903–1910.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all patients, their families and the clinicians involved for their cooperation. We thank Lies Vantomme and Shalina Baute for their expert technical assistance and Filip Pattyn for continuous support. Sarah Vergult is supported by a PhD fellowship of the Research Foundation – Flanders (FWO). Bart Loeys is senior clinical investigator of the Research Foundation – Flanders (FWO). This work was supported by a grant SBO60848 from the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation by Science and Technology in Flanders (IWT) and a Methusalem grant of the Flemish Government. This article presents research results of the Belgian program of Interuniversity Poles of attraction initiated by the Belgian State, Prime Minister's Office, Science Policy Programming (IUAP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vergult, S., Krgovic, D., Loeys, B. et al. Nasal speech and hypothyroidism are common hallmarks of 12q15 microdeletions. Eur J Hum Genet 19, 1032–1037 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.67
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.67
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
‘Nasal’ speech–hyper or hypo?
European Journal of Human Genetics (2012)
-
Nasal speech in patients with 12q15 microdeletions
European Journal of Human Genetics (2012)