Abstract
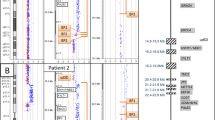
With the clinical implementation of genomic microarrays, the detection of cryptic unbalanced rearrangements in patients with syndromic developmental delay has improved considerably. Here we report the molecular karyotyping and phenotypic description of six new unrelated patients with partially overlapping microdeletions at 10p12.31p11.21 ranging from 1.0 to 10.6 Mb. The smallest region of overlap is 306 kb, which includes WAC gene, known to be associated with microtubule function and to have a role in cell division. Another patient has previously been described with a 10 Mb deletion, partially overlapping with our six patients. All seven patients have developmental delay and a majority of the patients have abnormal behaviour and dysmorphic features, including bulbous nasal tip, deep set eyes, synophrys/thick eyebrows and full cheeks, whereas other features varied. All patients also displayed various visual impairments and six out of seven patients had cardiac malformations. Taken together with the previously reported patient, our study suggests that the detected deletions may represent a new contiguous gene syndrome caused by dosage-sensitive genes that predispose to developmental delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR : Structural variation in the human genome and its role in disease. Annu Rev Med 2010; 61: 437–455.
Van Buggenhout G, Van Ravenswaaij-Arts C, Mc Maas N et al: The del(2)(q32.2q33) deletion syndrome defined by clinical and molecular characterization of four patients. Eur J Med Genet 2005; 48: 276–289.
Lynch SA, Foulds N, Thuresson AC et al: The 12q14 microdeletion syndrome: six new cases confirming the role of HMGA2 in growth. Eur J Hum Genet 2011; e-pub ahead of print 26 January 2011.
Menten B, Buysse K, Zahir F et al: Osteopoikilosis, short stature and mental retardation as key features of a new microdeletion syndrome on 12q14. J Med Genet 2007; 44: 264–268.
Shahdadpuri R, de Vries B, Pfundt R, de Leeuw N, Reardon W : Pseudoarthrosis of the clavicle and copper beaten skull associated with chromosome 10p11.21p12.1 microdeletion. Am J Med Genet A 2008; 146A: 233–237.
Stern RF, Roberts RG, Mann K, Yau SC, Berg J, Ogilvie CM : Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification using a completely synthetic probe set. Biotechniques 2004; 37: 399–405.
Thuresson AC, Bondeson ML, Edeby C et al: Whole-genome array-CGH for detection of submicroscopic chromosomal imbalances in children with mental retardation. Cytogenet Genome Res 2007; 118: 1–7.
Dauwerse JG, Jumelet EA, Wessels JW et al: Extensive cross-homology between the long and the short arm of chromosome 16 may explain leukemic inversions and translocations. Blood 1992; 79: 1299–1304.
Zhang F, Gu W, Hurles ME, Lupski JR : Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2009; 10: 451–481.
Szulwach KE, Jin P, Alisch RS : Noncoding RNAs in mental retardation. Clin Genet 2009; 75: 209–219.
Chen J, Bush JO, Ovitt CE, Lan Y, Jiang R : The TGF-beta pseudoreceptor gene Bambi is dispensable for mouse embryonic development and postnatal survival. Genesis 2007; 45: 482–486.
Tramullas M, Lantero A, Diaz A et al: BAMBI (bone morphogenetic protein and activin membrane-bound inhibitor) reveals the involvement of the transforming growth factor-beta family in pain modulation. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 1502–1511.
Goshima G, Mayer M, Zhang N, Stuurman N, Vale RD : Augmin: a protein complex required for centrosome-independent microtubule generation within the spindle. J Cell Biol 2008; 181: 421–429.
Meireles AM, Fisher KH, Colombie N, Wakefield JG, Ohkura H : Wac: a new Augmin subunit required for chromosome alignment but not for acentrosomal microtubule assembly in female meiosis. J Cell Biol 2009; 184: 777–784.
Jaglin XH, Chelly J : Tubulin-related cortical dysgeneses: microtubule dysfunction underlying neuronal migration defects. Trends Genet 2009; 25: 555–566.
Koolen DA, Vissers LE, Pfundt R et al: A new chromosome 17q21.31 microdeletion syndrome associated with a common inversion polymorphism. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 999–1001.
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the families for agreeing to participate in this study. This work was supported by grants from the Sävstaholm Society, the Borgström Foundation, Foundation Jerome Lejeune and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (ERS). ERS acknowledges the Michael Smith Foundation of Health Research Scholar Award. We are grateful for technical assistance and scientific discussion to Laure Lecerf, Audrey Briand and Sandra Whalen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wentzel, C., Rajcan-Separovic, E., Ruivenkamp, C. et al. Genomic and clinical characteristics of six patients with partially overlapping interstitial deletions at 10p12p11. Eur J Hum Genet 19, 959–964 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.71
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.71
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression analyses of WAC, a responsible gene for neurodevelopmental disorders, during mouse brain development
Medical Molecular Morphology (2023)
-
De novo loss-of-function mutations in WAC cause a recognizable intellectual disability syndrome and learning deficits in Drosophila
European Journal of Human Genetics (2016)
-
Prenatal and postnatal findings in a 10.6 Mb interstitial deletion at 10p11.22-p12.31
Journal of Human Genetics (2015)
-
Deletion at chromosome 10p11.23-p12.1 defines characteristic phenotypes with marked midface retrusion
Journal of Human Genetics (2012)