Abstract
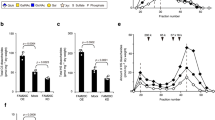
Costello syndrome is a pediatric genetic disorder linked to oncogenic germline mutations in the HRAS gene. The disease is characterized by multiple developmental abnormalities, as well as predisposition to malignancies. Our recent observation that heart tissue from patients with Costello syndrome showed a loss of the glycosaminoglycan chondroitin-4-sulfate (C4S) inspired our present study aimed to explore a functional involvement of the chondroitin sulfate (CS) biosynthesis gene Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11/Chondroitin-4-sulfotransferase-1 (CHST11/C4ST-1), as well as an impaired chondroitin sulfation balance, as a downstream mediator of oncogenic HRAS in Costello syndrome. Here we demonstrate a loss of C4S, as well as a reduction in C4ST-1 mRNA and protein expression, in primary fibroblasts from Costello syndrome patients. We go on to show that expression of oncogenic HRAS in normal fibroblasts can repress C4ST-1 expression, whereas interference with oncogenic HRAS signaling in Costello syndrome fibroblasts elevated C4ST-1 expression, thus identifying C4ST-1 as a negatively regulated target gene of HRAS signaling. Importantly, we show that forced expression of C4ST-1 in Costello fibroblasts could rescue the proliferation and elastogenesis defects associated with oncogenic HRAS signaling in these cells. Our results indicate reduced C4ST-1 expression and chondroitin sulfation imbalance mediating the effects of oncogenic HRAS signaling in the pathogenesis of Costello syndrome. Thus, our work identifies C4ST-1-dependent chondroitin sulfation as a downstream vulnerability in oncogenic RAS signaling, which might be pharmacologically exploited in future treatments of not only Costello syndrome and other RASopathies, but also human cancers associated with activating RAS mutations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Costello JM : A new syndrome: mental subnormality and nasal papillomata. Aust Paediatr J 1977; 13: 114–118.
Costello JM : Costello syndrome: update on the original cases and commentary. Am J Med Genet 1996; 62: 199–201.
Digilio MC, Sarkozy A, Capolino R et al: Costello syndrome: clinical diagnosis in the first year of life. Eur J Pediatr 2008; 167: 621–628.
Hennekam RC : Costello syndrome: an overview. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2003; 117C: 42–48.
Johnson JP, Golabi M, Norton ME et al: Costello syndrome: phenotype, natural history, differential diagnosis, and possible cause. J Pediatr 1998; 133: 441–448.
Mancini GM, van Diggelen OP, Kleijer WJ et al: Studies on the pathogenesis of Costello syndrome. J Med Genet 2003; 40: e37.
Rauen KA, Hefner E, Carrillo K et al: Molecular aspects, clinical aspects and possible treatment modalities for Costello syndrome: Proceedings from the 1st International Costello Syndrome Research Symposium 2007. Am J Med Genet A 2008; 146A: 1205–1217.
Zenker M : Clinical manifestations of mutations in RAS and related intracellular signal transduction factors. Curr Opin Pediatr 2011; 23: 443–451.
Gripp KW : Tumor predisposition in Costello syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2005; 137C: 72–77.
Aoki Y, Niihori T, Kawame H et al: Germline mutations in HRAS proto-oncogene cause Costello syndrome. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 1038–1040.
Estep AL, Tidyman WE, Teitell MA, Cotter PD, Rauen KA : HRAS mutations in Costello syndrome: detection of constitutional activating mutations in codon 12 and 13 and loss of wild-type allele in malignancy. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 8–16.
Gripp KW, Lin AE, Stabley DL et al: HRAS mutation analysis in Costello syndrome: genotype and phenotype correlation. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 1–7.
Kerr B, Delrue MA, Sigaudy S et al: Genotype-phenotype correlation in Costello syndrome: HRAS mutation analysis in 43 cases. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 401–405.
Kratz CP, Niemeyer CM, Zenker M : An unexpected new role of mutant Ras: perturbation of human embryonic development. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007; 85: 227–235.
Rauen KA : HRAS and the Costello syndrome. Clin Genet 2007; 71: 101–108.
Sol-Church K, Stabley DL, Demmer LA et al: Male-to-male transmission of Costello syndrome: G12S HRAS germline mutation inherited from a father with somatic mosaicism. Am J Med Genet A 2009; 149A: 315–321.
Zampino G, Pantaleoni F, Carta C et al: Diversity, parental germline origin, and phenotypic spectrum of de novo HRAS missense changes in Costello syndrome. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 265–272.
Rauen KA, Banerjee A, Bishop WR et al: Costello and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndromes: moving toward clinical trials in RASopathies. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2011; 157: 136–146.
Tidyman WE, Rauen KA : Noonan, Costello and cardio-facio-cutaneous syndromes: dysregulation of the Ras-MAPK pathway. Expert Rev Mol Med 2008; 10: e37.
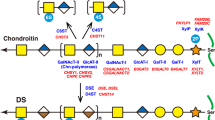
Habuchi O : Diversity and functions of glycosaminoglycan sulfotransferases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000; 1474: 115–127.
Klüppel M : The roles of chondroitin-4-sulfotransferase-1 in development and disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2010; 93: 113–132.
Kusche-Gullberg M, Kjellen L : Sulfotransferases in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2003; 13: 605–611.
Sugahara K, Kitagawa H : Recent advances in the study of the biosynthesis and functions of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2000; 10: 518–527.
Klüppel M, Wight TN, Chan C, Hinek A, Wrana JL : Maintenance of chondroitin sulfation balance by chondroitin-4-sulfotransferase 1 is required for chondrocyte development and growth factor signaling during cartilage morphogenesis. Development 2005; 132: 3989–4003.
Properzi F, Carulli D, Asher RA et al: Chondroitin 6-sulphate synthesis is up-regulated in injured CNS, induced by injury-related cytokines and enhanced in axon-growth inhibitory glia. Eur J Neurosci 2005; 21: 378–390.
Ricciardelli C, Quinn DI, Raymond WA et al: Elevated levels of peritumoral chondroitin sulfate are predictive of poor prognosis in patients treated by radical prostatectomy for early-stage prostate cancer. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2324–2328.
Ricciardelli C, Sakko AJ, Stahl J, Tilley WD, Marshall VR, Horsfall DJ : Prostatic chondroitin sulfate is increased in patients with metastatic disease but does not predict survival outcome. Prostate 2009; 69: 761–769.
Sakko AJ, Butler MS, Byers S et al: Immunohistochemical level of unsulfated chondroitin disaccharides in the cancer stroma is an independent predictor of prostate cancer relapse. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008; 17: 2488–2497.
Suwiwat S, Ricciardelli C, Tammi R et al: Expression of extracellular matrix components versican, chondroitin sulfate, tenascin, and hyaluronan, and their association with disease outcome in node-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 2491–2498.
Teng YH, Tan PH, Chia SJ et al: Increased expression of non-sulfated chondroitin correlates with adverse clinicopathological parameters in prostate cancer. Mod Pathol 2008; 21: 893–901.
Vijayagopal P, Figueroa JE, Levine EA : Altered composition and increased endothelial cell proliferative activity of proteoglycans isolated from breast carcinoma. J Surg Oncol 1998; 68: 250–254.
Klüppel M, Vallis KA, Wrana JL : A high-throughput induction gene trap approach defines C4ST as a target of BMP signaling. Mech Dev 2002; 118: 77–89.
Lopes CC, Toma L, Pinhal MA et al: EJ-ras oncogene transfection of endothelial cells upregulates the expression of syndecan-4 and downregulates heparan sulfate sulfotransferases and epimerase. Biochimie 2006; 88: 1493–1504.
Romaris M, Villena J, Molist A, Heredia A, Bassols A : Ras transformation alters the composition of extracellular matrix proteoglycans in rat fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994; 200: 925–932.
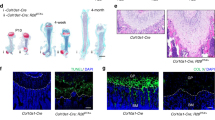
Hinek A, Smith AC, Cutiongco EM, Callahan JW, Gripp KW, Weksberg R : Decreased elastin deposition and high proliferation of fibroblasts from Costello syndrome are related to functional deficiency in the 67-kD elastin-binding protein. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 859–872.
Hinek A, Teitell MA, Schoyer L et al: Myocardial storage of chondroitin sulfate-containing moieties in Costello syndrome patients with severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Med Genet A 2005; 133A: 1–12.
Jorge AA, Malaquias AC, Arnhold IJ, Mendonca BB : Noonan syndrome and related disorders: a review of clinical features and mutations in genes of the RAS/MAPK pathway. Horm Res 2009; 71: 185–193.
Gremer L, Merbitz-Zahradnik T, Dvorsky R et al: Germline KRAS mutations cause aberrant biochemical and physical properties leading to developmental disorders. Hum Mutat 2011; 32: 33–43.
Niihori T, Aoki Y, Okamoto N et al: HRAS mutants identified in Costello syndrome patients can induce cellular senescence: possible implications for the pathogenesis of Costello syndrome. J Hum Genet 2011; 56: 707–715.
Hatamochi A, Nagayama H, Kuroda K et al: Costello syndrome with decreased gene expression of elastin in cultured dermal fibroblasts. Dermatology 2000; 201: 366–369.
Hinek A, Braun KR, Liu K, Wang Y, Wight TN : Retrovirally mediated overexpression of versican v3 reverses impaired elastogenesis and heightened proliferation exhibited by fibroblasts from Costello syndrome and Hurler disease patients. Am J Pathol 2004; 164: 119–131.
Mori M, Yamagata T, Mori Y et al: Elastic fiber degeneration in Costello syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1996; 61: 304–309.
Tatano Y, Fujinawa R, Kozutsumi Y et al: Tropoelastin regulates chemokine expression in fibroblasts in Costello syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 372: 681–687.
Bos JL : ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res 1989; 49: 4682–4689.
Uebelhart D : Clinical review of chondroitin sulfate in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2008; 16 (Suppl 3): S19–S21.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) to AH and JLW and by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario to AH. MK was supported by a CIHR postdoctoral fellowship. JLW is a CIHR investigator and an International Research Scholar of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klüppel, M., Samavarchi-Tehrani, P., Liu, K. et al. C4ST-1/CHST11-controlled chondroitin sulfation interferes with oncogenic HRAS signaling in Costello syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 20, 870–877 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vulnerability to shear stress caused by altered peri-endothelial matrix is a key feature of Moyamoya disease
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Chondroitin 6-sulfate represses keratinocyte proliferation in mouse skin, which is associated with psoriasis
Communications Biology (2021)
-
CHST11/13 Regulate the Metastasis and Chemosensitivity of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Via Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2016)