Abstract
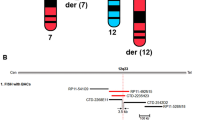
The 2q37 locus is one of the most commonly deleted subtelomeric regions. Such a deletion has been identified in >100 patients by telomeric fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis and, less frequently, by array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH). A recognizable ‘2q37-deletion syndrome’ or Albright’s hereditary osteodystrophy-like syndrome has been previously described. To better map the deletion and further refine this deletional syndrome, we formed a collaboration with the Association of French Language Cytogeneticists to collect 14 new intellectually deficient patients with a distal or interstitial 2q37 deletion characterized by FISH and array-CGH. Patients exhibited facial dysmorphism (13/14) and brachydactyly (10/14), associated with behavioural problems, autism or autism spectrum disorders of varying severity and overweight or obesity. The deletions in these 14 new patients measured from 2.6 to 8.8 Mb. Although the major role of HDAC4 has been demonstrated, the phenotypic involvement of several other genes in the deleted regions is unknown. We further refined the genotype–phenotype correlation for the 2q37 deletion. To do this, we examined the smallest overlapping deleted region for candidate genes for skeletal malformations (facial dysmorphism and brachydactyly), overweight, behavioural problems and seizures, using clinical data, a review of the literature, and the Manteia database. Among the candidate genes identified, we focus on the roles of PRLH, PER2, TWIST2, CAPN10, KIF1A, FARP2, D2HGDH and PDCD1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Balikova I, Vermeesch JR, Fryns JP, Van Esch H : Bronchiectasis and immune deficiency in an adult patient with deletion 2q37 due to an unbalanced translocation t(2;10). Eur J Med Genet 2009; 52: 260–261.
Chen CP, Lin SP, Chern SR et al: Deletion 2q37.3->qter and duplication 15q24.3->qter characterized by array CGH in a girl with epilepsy and dysmorphic features. Genet Couns 2010; 21: 263–267.
Cusco I, del Campo M, Vilardell M et al: Array-CGH in patients with Kabuki-like phenotype: identification of two patients with complex rearrangements including 2q37 deletions and no other recurrent aberration. BMC Med Genet 2008; 9: 27.
Devillard F, Guinchat V, Moreno-De-Luca D et al: Paracentric inversion of chromosome 2 associated with cryptic duplication of 2q14 and deletion of 2q37 in a patient with autism. Am J Med Genet A 2010; 152A: 2346–2354.
Felder B, Radlwimmer B, Benner A et al: FARP2, HDLBP and PASK are downregulated in a patient with autism and 2q37.3 deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 2009; 149A: 952–959.
Kariminejad A, Kariminejad R, Tzschach A et al: Craniosynostosis in a patient with 2q37.3 deletion 5q34 duplication: association of extra copy of MSX2 with craniosynostosis. Am J Med Genet A 2009; 149A: 1544–1549.
Kitsiou-Tzeli S, Sismani C, Ioannides M et al: Array-CGH analysis and clinical description of 2q37.3 de novo subtelomeric deletion. Eur J Med Genet 2007; 50: 73–78.
Mazzone L, Vassena L, Ruta L, Mugno D, Galesi O, Fichera M : Brief report: peculiar evolution of autistic behaviors in two unrelated children with brachidactyly-mental retardation syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord 2012; 42: 2202–2207.
Vera-Carbonell A, Lopez-Exposito I, Bafalliu JA et al: Molecular characterization of a new patient with a non-recurrent inv dup del 2q and review of the mechanisms for this rearrangement. Am J Med Genet A 2010; 152A: 2670–2680.
Williams SR, Aldred MA, Der Kaloustian VM et al: Haploinsufficiency of HDAC4 causes brachydactyly mental retardation syndrome, with brachydactyly type E, developmental delays, and behavioral problems. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 87: 219–228.
Davids MS, Crawford E, Weremowicz S et al: STK25 is a candidate gene for pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. Genomics 2001; 77: 2–4.
Falk RE, Casas KA : Chromosome 2q37 deletion: clinical and molecular aspects. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2007; 145C: 357–371.
Lukusa T, Vermeesch JR, Holvoet M, Fryns JP, Devriendt K : Deletion 2q37.3 and autism: molecular cytogenetic mapping of the candidate region for autistic disorder. Genet Couns 2004; 15: 293–301.
Shrimpton AE, Braddock BR, Thomson LL, Stein CK, Hoo JJ : Molecular delineation of deletions on 2q37.3 in three cases with an Albright hereditary osteodystrophy-like phenotype. Clin Genet 2004; 66: 537–544.
Smith M, Escamilla JR, Filipek P et al: Molecular genetic delineation of 2q37.3 deletion in autism and osteodystrophy: report of a case and of new markers for deletion screening by PCR. Cytogenet Cell Genet 2001; 94: 15–22.
Syrrou M, Keymolen K, Devriendt K et al: Glypican 1 gene: good candidate for brachydactyly type E. Am J Med Genet 2002; 108: 310–314.
Wassink TH, Piven J, Vieland VJ et al: Evaluation of the chromosome 2q37.3 gene CENTG2 as an autism susceptibility gene. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 136B: 36–44.
Ravnan JB, Tepperberg JH, Papenhausen P et al: Subtelomere FISH analysis of 11 688 cases: an evaluation of the frequency and pattern of subtelomere rearrangements in individuals with developmental disabilities. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 478–489.
Knight SJ, Lese CM, Precht KS et al: An optimized set of human telomere clones for studying telomere integrity and architecture. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 320–332.
Aldred MA, Sanford RO, Thomas NS et al: Molecular analysis of 20 patients with 2q37.3 monosomy: definition of minimum deletion intervals for key phenotypes. J Med Genet 2004; 41: 433–439.
Armstrong L, Allanson JE, Weaver DD, Bevan CJ, Hobart HH : Unrelated patients with a rearrangement of chromosome 2 causing duplication of 2p23 and deletion of 2q37. Am J Med Genet A 2005; 134: 299–304.
Burd L, Martsolf JT, Kerbeshian J, Jalal SM : Partial 6p trisomy associated with infantile autism. Clin Genet 1988; 33: 356–359.
Casas KA, Mononen TK, Mikail CN et al: Chromosome 2q terminal deletion: report of 6 new patients and review of phenotype-breakpoint correlations in 66 individuals. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 130A: 331–339.
Chaabouni M, Le Merrer M, Raoul O et al: Molecular cytogenetic analysis of five 2q37 deletions: refining the brachydactyly candidate region. Eur J Med Genet 2006; 49: 255–263.
Chassaing N, De Mas P, Tauber M et al: Molecular characterization of a cryptic 2q37 deletion in a patient with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy-like phenotype. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 128A: 410–413.
Fernandez-Rebollo E, Perez O, Martinez-Bouzas C et al: Two cases of deletion 2q37 associated with segregation of an unbalanced translocation 2;21: choanal atresia leading to misdiagnosis of CHARGE syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol 2009; 160: 711–717.
Galasso C, Lo-Castro A, Lalli C, Nardone AM, Gullotta F, Curatolo P : Deletion 2q37: an identifiable clinical syndrome with mental retardation and autism. J Child Neurol 2008; 23: 802–806.
Giardino D, Finelli P, Gottardi G et al: Cryptic subtelomeric translocation t(2;16)(q37;q24) segregating in a family with unexplained stillbirths and a dysmorphic, slightly retarded child. Eur J Hum Genet 2001; 9: 881–886.
Grammatico P, Majore S, Marrocco G et al: 46,XX,der(2)t(2;10)(2pter-->2q37::10p13-->10pter)[127]/45,X,der(2)t(2;10) (2pter-->2q37::10p13-->10pter)[23]. Karyotype-phenotype correlation and genetic counselling in complex karyotypes. Genet Couns 1999; 10: 351–358.
Lukusa T, Smeets E, Vogels A, Vermeesch JR, Fryns JP : Terminal 2q37 deletion and autistic behaviour. Genet Couns 2005; 16: 179–180.
Sanchez JM, Pantano AM : A case of deletion 2q35 – qter and a peculiar phenotype. J Med Genet 1984; 21: 147–149.
Sogaard M, Tumer Z, Hjalgrim H et al: Subtelomeric study of 132 patients with mental retardation reveals 9 chromosomal anomalies and contributes to the delineation of submicroscopic deletions of 1pter, 2qter, 4pter, 5qter and 9qter. BMC Med Genet 2005; 6: 21.
Wiktor A, Feldman GL, Bawle EV, Czarnecki P, Conard JV, Van Dyke DL : Deletion of 2q37 and duplication of 10q24: two cases in the same family and review of the literature. Ann Genet 2001; 44: 129–134.
Fan YS, Zhang Y, Speevak M, Farrell S, Jung JH, Siu VM : Detection of submicroscopic aberrations in patients with unexplained mental retardation by fluorescence in situ hybridization using multiple subtelomeric probes. Genet Med 2001; 3: 416–421.
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T : Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 1999; 11: 141–151.
Maletinska L, Spolcova A, Maixnerova J, Blechova M, Zelezna B : Biological properties of prolactin-releasing peptide analogs with a modified aromatic ring of a C-terminal phenylalanine amide. Peptides 2011; 32: 1887–1892.
Takayanagi Y, Onaka T : Roles of prolactin-releasing peptide and RFamide related peptides in the control of stress and food intake. FEBS J 2010; 277: 4998–5005.
Doherty ES, Solomon BD, Lacbawan F : 2q37 Deletion Syndrome; in Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Stephens K, (Hrsg) (eds): Gene Reviews Seattle/WA: University of Washington, 1993.
Sosic D, Richardson JA, Yu K, Ornitz DM, Olson EN : Twist regulates cytokine gene expression through a negative feedback loop that represses NF-kappaB activity. Cell 2003; 112: 169–180.
Vermeesch JR, Thoelen R, Fryns JP : A familial complex chromosome translocation resulting in duplication of 6p25. Ann Genet 2004; 47: 275–280.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families. We thank our colleagues in the ACLF network ‘mapping the subtelomeric regions/clinical and molecular phenotype’. This work was funded by the following grants: AOL 2001 and AOL 2003, PHRC 2003 CHU REIMS, DHOS/OPRC/2007/35 and 455 France. The manuscript was prepared with the editorial help from Gap Junction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leroy, C., Landais, E., Briault, S. et al. The 2q37-deletion syndrome: an update of the clinical spectrum including overweight, brachydactyly and behavioural features in 14 new patients. Eur J Hum Genet 21, 602–612 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.230
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2012.230
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Brain-specific Pd1 deficiency leads to cortical neurogenesis defects and depressive-like behaviors in mice
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
2q37 deletion syndrome in a Colombian patient with macrocephaly: a case report
BMC Pediatrics (2022)
-
High-resolution chromosomal microarray analysis for copy-number variations in high-functioning autism reveals large aberration typical for intellectual disability
Journal of Neural Transmission (2020)
-
Association of GNAS imprinting defects and deletions of chromosome 2 in two patients: clues explaining phenotypic heterogeneity in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1B/iPPSD3
Clinical Epigenetics (2019)
-
Chromosomal microarray analysis in the genetic evaluation of 279 patients with syndromic obesity
Molecular Cytogenetics (2018)