Abstract
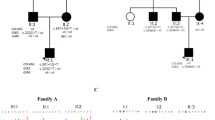
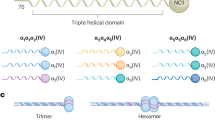
Hereditary hearing loss is the most common human sensorineural disorder. Genetic causes are highly heterogeneous, with mutations detected in >40 genes associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss, to date. Whereas autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance is prevalent, X-linked forms of nonsyndromic hearing impairment are extremely rare. Here, we present a Hungarian three-generation family with X-linked nonsyndromic congenital hearing loss and the underlying genetic defect. Next-generation sequencing and subsequent segregation analysis detected a missense mutation (c.1771G>A, p.Gly591Ser) in the type IV collagen gene COL4A6 in all affected family members. Bioinformatic analysis and expression studies support this substitution as being causative. COL4A6 encodes the alpha-6 chain of type IV collagen of basal membranes, which forms a heterotrimer with two alpha-5 chains encoded by COL4A5. Whereas mutations in COL4A5 and contiguous X-chromosomal deletions involving COL4A5 and COL4A6 are associated with X-linked Alport syndrome, a nephropathy associated with deafness and cataract, mutations in COL4A6 alone have not been related to any hereditary disease so far. Moreover, our index patient and other affected family members show normal renal and ocular function, which is not consistent with Alport syndrome, but with a nonsyndromic type of hearing loss. In situ hybridization and immunostaining demonstrated expression of the COL4A6 homologs in the otic vesicle of the zebrafish and in the murine inner ear, supporting its role in normal ear development and function. In conclusion, our results suggest COL4A6 as being the fourth gene associated with X-linked nonsyndromic hearing loss.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bayazit YA, Yilmaz M : An overview of hereditary hearing loss. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 2006; 68: 57–63.
Yan D, Liu XZ : Genetics and pathological mechanisms of Usher syndrome. J Hum Genet 2010; 55: 327–335.
Kokotas H, Petersen MB, Willems PJ : Mitochondrial deafness. Clin Genet 2007; 71: 379–391.
Kelsell DP, Dunlop J, Stevens HP et al: Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature 1997; 387: 80–83.
Tekin M, Arnos KS, Pandya A : Advances in hereditary deafness. Lancet 2001; 358: 1082–1090.
Liu X, Han D, Li J et al: Loss-of-function mutations in the PRPS1 gene cause a type of nonsyndromic X-linked sensorineural deafness, DFN2. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 86: 65–71.
de Kok YJ, van der Maarel SM, Bitner-Glindzicz M et al: Association between X-linked mixed deafness and mutations in the POU domain gene POU3F4. Science 1995; 267: 685–688.
Huebner AK, Gandia M, Frommolt P et al: Nonsense mutations in SMPX, encoding a protein responsive to physical force, result in X-chromosomal hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 621–627.
Schraders M, Haas SA, Weegerink NJ et al: Next-generation sequencing identifies mutations of SMPX, which encodes the small muscle protein, X-linked, as a cause of progressive hearing impairment. Am J Hum Genet 2011; 88: 628–634.
Lalwani AK, Brister JR, Fex J et al: A new nonsyndromic X-linked sensorineural hearing impairment linked to Xp21.2. Am J Hum Genet 1994; 55: 685–694.
Pfister MH, Apaydin F, Turan O et al: A second family with nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss linked to Xp21.2: refinement of the DFN4 locus within DMD. Genomics 1998; 53: 377–382.
Li H, Durbin R : Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 1754–1760.
Koboldt DC, Chen K, Wylie T et al: VarScan: variant detection in massively parallel sequencing of individual and pooled samples. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2283–2285.
Corpet F : Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucl Acids Res 1988; 16: 10881–10890.
Cosgrove D, Samuelson G, Pinnt J : Immunohistochemical localization of basement membrane collagens and associated proteins in the murine cochlea. Hear Res 1996; 97: 54–65.
Winkler C, Schafer M, Duschl J, Schartl M, Volff JN : Functional divergence of two zebrafish midkine growth factors following fish-specific gene duplication. Genome Res 2003; 13: 1067–1081.
Buchman CA, Copeland BJ, Yu KK, Brown CJ, Carrasco VN, Pillsbury HC : Cochlear implantation in children with congenital inner ear malformations. Laryngoscope 2004; 114: 309–316.
Ricard-Blum S : The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3: a004978.
Dalgleish R : The human collagen mutation database 1998. Nucleic Acids Res 1998; 26: 253–255.
Borza DB, Bondar O, Ninomiya Y et al: The NC1 domain of collagen IV encodes a novel network composed of the alpha 1, alpha 2, alpha 5, and alpha 6 chains in smooth muscle basement membranes. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 28532–28540.
Sugimoto M, Oohashi T, Ninomiya Y : The genes COL4A5 and COL4A6, coding for basement membrane collagen chains alpha 5(IV) and alpha 6(IV), are located head-to-head in close proximity on human chromosome Xq22 and COL4A6 is transcribed from two alternative promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 11679–11683.
Segal Y, Zhuang L, Rondeau E, Sraer JD, Zhou J : Regulation of the paired type IV collagen genes COL4A5 and COL4A6. Role of the proximal promoter region. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 11791–11797.
Kashtan CE : Alport syndrome: an inherited disorder of renal, ocular, and cochlear basement membranes. Medicine 1999; 78: 338–360.
Cochat P, Guibaud P, Garcia-Torres R, Roussel B, Guarner V, Larbre F : Diffuse leiomyomatosis in Alport syndrome. J Pediatr 1988; 113: 339–343.
Anker MC, Arnemann J, Neumann K, Ahrens P, Schmidt H, Konig R : Alport syndrome with diffuse leiomyomatosis. Am J Med Genet 2003; 119A: 381–385.
de Kok YJ, Vossenaar ER, Cremers CW et al: Identification of a hot spot for microdeletions in patients with X-linked deafness type 3 (DFN3) 900 kb proximal to the DFN3 gene POU3F4. Hum Mol Genet 1996; 5: 1229–1235.
Song MH, Lee HK, Choi JY, Kim S, Bok J, Kim UK : Clinical evaluation of DFN3 patients with deletions in the POU3F4 locus and detection of carrier female using MLPA. Clin Genet 2010; 78: 524–532.
Acknowledgements
We are deeply grateful to all the family members for their participation in this study, and to Dr Jörg Schröder, Professor Wafaa Shehata-Dieler and Professor Annerose Keilmann for clinical support. We thank Professor Tiemo Grimm for calculation of the LOD scores, Dr Eberhard Schneider for inspecting radiographs of patients with hearing loss, and Dr Wolfram Kress for constructive discussions. We appreciate the donation of control samples by Dr Veronika Karcagi and Dr Ulrich Zechner. We also thank Professor Manfred Schartl for his support with the whole-mount in situ experiment in zebrafish embryos. Additionally, we would like to thank Simone Günther, Birgit Halliger-Keller, Jens Gräf and Mohammed Uddin for technical assistance. This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (HA 1374/7–2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rost, S., Bach, E., Neuner, C. et al. Novel form of X-linked nonsyndromic hearing loss with cochlear malformation caused by a mutation in the type IV collagen gene COL4A6. Eur J Hum Genet 22, 208–215 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2013.108
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Deafness—family matters
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
Confirmation of COL4A6 variants in X-linked nonsyndromic hearing loss and its clinical implications
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
The link between inner ear malformations and the rest of the body: what we know so far about genetic, imaging and histology
Neuroradiology (2020)
-
Clinical and molecular characterization of POU3F4 mutations in multiple DFNX2 Chinese families
BMC Medical Genetics (2018)
-
A novel mutation in the SMPX gene associated with X-linked nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss in a Chinese family
Journal of Human Genetics (2018)