Abstract
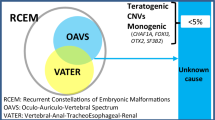
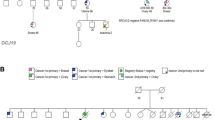
Oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (OAVS) is a developmental disorder characterized by hemifacial microsomia associated with ear, eyes and vertebrae malformations showing highly variable expressivity. Recently, MYT1, encoding the myelin transcription factor 1, was reported as the first gene involved in OAVS, within the retinoic acid (RA) pathway. Fifty-seven OAVS patients originating from Brazil were screened for MYT1 variants. A novel de novo missense variant affecting function, c.323C>T (p.(Ser108Leu)), was identified in MYT1, in a patient presenting with a severe form of OAVS. Functional studies showed that MYT1 overexpression downregulated all RA receptors genes (RARA, RARB, RARG), involved in RA-mediated transcription, whereas no effect was observed on CYP26A1 expression, the major enzyme involved in RA degradation, Moreover, MYT1 variants impacted significantly the expression of these genes, further supporting their pathogenicity. In conclusion, a third variant affecting function in MYT1 was identified as a cause of OAVS. Furthermore, we confirmed MYT1 connection to RA signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barisic I, Odak L, Loane M et al: Prevalence, prenatal diagnosis and clinical features of oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum: a registry-based study in Europe. Eur J Hum Genet 2014; 22: 1026–1033.
Lopez E, Berenguer M, Tingaud-Sequeira A et al: Mutations in MYT1, encoding the myelin transcription factor 1, are a rare cause of OAVS. J Med Genet 2016; 53: 752–760.
Lammer EJ, Chen DT, Hoar RM et al: Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med 1985; 313: 837–841.
Rooryck C, Souakri N, Cailley D et al: Array-CGH analysis of a cohort of 86 patients with oculoauriculovertebral spectrum. Am J Med Genet 2010; 152A: 1984–1989.
Beleza-Meireles A, Clayton-Smith J, Saraiva JM, Tassabehji M : Oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum: a review of the literature and genetic update. J Med Genet 2014; 51: 635–645.
Tasse C, Böhringer S, Fischer S et al: Oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (OAVS): clinical evaluation and severity scoring of 53 patients and proposal for a new classification. Eur J Med Genet 2005; 48: 397–411.
Vasconcelos FF, Sessa A, Laranjeira C et al: MyT1 counteracts the neural progenitor program to promote vertebrate neurogenesis. Cell Rep 2016; 17: 469–483.
Srour M, Chitayat D, Caron V et al: Recessive and dominant mutations in retinoic acid receptor beta in cases with microphthalmia and diaphragmatic Hernia. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 93: 765–772.
Baroni T, Bellucci C, Lilli C et al: Retinoic acid, GABA-ergic, and TGF-beta signaling systems are involved in human cleft palate fibroblast phenotype. Mol Med Camb Mass 2006; 12: 237–245.
Elmazar MMA, Rühl R, Reichert U, Shroot B, Nau H : RAR α-mediated teratogenicity in mice is potentiated by an rxr agonist and reduced by an RAR antagonist: dissection of retinoid receptor-induced pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1997; 146: 21–28.
Matt N, Ghyselinck NB, Wendling O, Chambon P, Mark M : Retinoic acid-induced developmental defects are mediated by RARβ/RXR heterodimers in the pharyngeal endoderm. Development 2003; 130: 2083–2093.
Smith DP, Mason CS, Jones E, Old R : Expression of a dominant negative retinoic acid receptor γ in Xenopus embryos leads to partial resistance to retinoic acid. Rouxs Arch Dev Biol 1993; 203: 254–265.
Ross AC, Zolfaghari R : Cytochrome P450s in the regulation of cellular retinoic acid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 2011; 31: 65–87.
Lee LMY, Leung C-Y, Tang WWC et al: A paradoxical teratogenic mechanism for retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2012; 109: 13668–13673.
Maynard TM, Gopalakrishna D, Meechan DW, Paronett EM, Newbern JM, LaMantia A-S : 22q11 Gene dosage establishes an adaptive range for sonic hedgehog and retinoic acid signaling during early development. Hum Mol Genet 2013; 22: 300–312.
Digilio MC, McDonald-McGinn DM, Heike C et al: Three patients with oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum and microdeletion 22q11.2. Am J Med Genet A 2009; 149A: 2860–2864.
Colovati MES, Bragagnolo S, Guilherme RS et al: Atypical 581-kb 22q11.21 deletion in a patient with oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum phenotype. Cytogenet Genome Res 2015; 147: 130–134.
Loudig O, Babichuk C, White J, Abu-Abed S, Mueller C, Petkovich M : Cytochrome P450RAI(CYP26) promoter: a distinct composite retinoic acid response element underlies the complex regulation of retinoic acid metabolism. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 1483–1497.
Abu-Abed S, Dollé P, Metzger D, Beckett B, Chambon P, Petkovich M : The retinoic acid-metabolizing enzyme, CYP26A1, is essential for normal hindbrain patterning, vertebral identity, and development of posterior structures. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 226–240.
Matsushita F, Kameyama T, Kadokawa Y, Marunouchi T : Spatiotemporal expression pattern of Myt/NZF family zinc finger transcription factors during mouse nervous system development. Dev Dyn Off Publ Am Assoc Anat 2014; 243: 588–600.
Dollé P, Fraulob V, Gallego-Llamas J, Vermot J, Niederreither K : Fate of retinoic acid–activated embryonic cell lineages. Dev Dyn 2010; 239: 3260–3274.
Duester G : Retinoic acid regulation of the somitogenesis clock. Birth Defects Res Part C Embryo Today Rev 2007; 81: 84–92.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ANR (Agence Nationale pour la Recherche, ANR-12-JVS1-0002), the University Hospital of Bordeaux (Appel Offre Interne GOLDGEN 2012), the Fondation Maladies Rares, and the Ministry of Research and Higher Education (PhD fellowship for MB) and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), Brazil. We thank Mr MARIE Yannick (in ICM in La Pitié Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France) for his technical support during sequencing by GS Junior Technology. We also thank the patients and their families.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berenguer, M., Tingaud-Sequeira, A., Colovati, M. et al. A novel de novo mutation in MYT1, the unique OAVS gene identified so far. Eur J Hum Genet 25, 1083–1086 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2017.101
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2017.101
This article is cited by
-
Novel variants in FOXI3 gene confirm its implication in Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral spectrum
European Journal of Human Genetics (2025)
-
A recurrent missense variant in EYA3 gene is associated with oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum
Human Genetics (2021)
-
Prenatal retinoic acid exposure reveals candidate genes for craniofacial disorders
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Oculoauriculovertebral spectrum and maxillary sinus volumes
Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics / Fortschritte der Kieferorthopädie (2018)