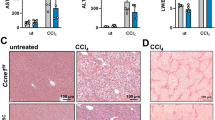
Abstract
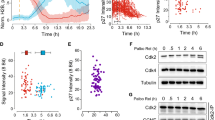
The changes of cell cycle regulators which may trigger G0 to G1 transition during liver regeneration have been examined. In vivo thymidine uptake indicated that S phase began about 18 h and the peak of DNA synthesis appeared from 21 to 24 h after partial hepatectomy. Various time-points from G0 to mid-S-phase were selected within 24 h after partial hepatectomy and the expression levels of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) and cyclindependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) were examined by Northern and Western analysis. Both cyclin D1 mRNA and protein increased at 15 h after operation. Cyclin E mRNA was first detected at 12 h and continued to increase until 21 h, whereas expression of cyclin B mRNA was first observed at 21 h. Expression of Cdk4 mRNA in normal rat liver was clearly detectable, increased significantly at 9 h after resection, and remained increased up to 24 h. On the other hand, an increase in Cdk4 protein was observed as early as 3 h after the surgery and reached plateau at 18 h. We next examined expression of CKIs which may regulate activity of cyclin/Cdk complex during liver regeneration. p 2 7K I P 1 protein was detected in normal rat liver whereas p21C I P 1 protein was not. Expression of p 2 1C I P 1 protein appeared as early as 3 h and continued to increase up to 21 h. Expression of p27KIP1 protein, however, increased slightly until 24 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, H., Lim, I. & Lee, JH. Changes in the expression of cell cycle regulators during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Exp Mol Med 28, 187–191 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1996.29
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1996.29