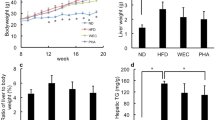
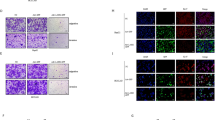
Abstract
An accelerating effect of methyl-deficient diet (MDD) on hepatocarcinogenesis and methylation pattern of nuclear protein(s) by S-adenosylmethionine: protein arginine N-methyltransferase (protein methylase I, PM-I) have been studied with 3'-methyl-4-dimethyl- aminoazobenzene(MeDAB)-treated rats. The MDD+MeDAB-fed group produced typical cancer cells in the liver almost two weeks earlier than the control synthetic diet (CSD)+MeDAB-fed group. Protein methylase I (PM-I) activity in the livers of MDD alone fed rats began to increase at around 2 weeks after MDD-feeding, reaching a peak at 4 weeks and declining thereafter. When nuclei isolated either from normal livers or from cholangiocarcinoma cells were incubated with PM-I preparation from normal liver, 16 and 23-kDa nuclear proteins were the major methylated proteins, regardless of the source of the nuclei. However, when the above mentioned nuclei were incubated with PM-I preparations either from MDD alone fed livers or MDD+ MeDAB-induced cholangiocarcinoma cells, the methylation of 23-kDa protein was not detected. The result suggests that there is a hitherto-unknown PM-I specific to 23 kDa nuclear protein which was lost during methyl deficient diet feeding and hepatocarcinogenesis. The N-terminal 20 amino acids sequence of the 23-kDa protein was found to be (1)Gly-Val-Pro-Leu-(5)X-Arg-Leu-Phe-Asp-(10)His-Ala-Met-Leu-Gln-(15)Ala -His-Arg-Ala-His-(20)Glu, having 94.7% sequence homology with human chorionic somatomammotropin precursor A and B.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Paik, MK., Han, YJ., Hong, JH. et al. Protein methylation in cellular proliferation and differentiation: non-histone nuclear methyl acceptor protein(s) during 3'-methyl-4-dimethylaminoazobenzene-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Exp Mol Med 29, 35–43 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1997.6
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1997.6