Abstract
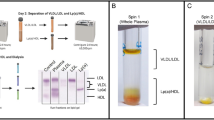
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) is known to be attached to the luminal surface of vascular endothelial cells in a complex with membrane-bound heparan sulfate, and released into blood stream by heparin. LPL that catalyzes hydrolysis of triglyceride (TGL) on chylomicron and VLDL into two fatty acids and monoacylglycerol, is also implicated to participate in an enhancement of cholesterol uptake by arterial endothelial cells in vitro. But little is known about the LPL-mediated cholesterol uptake in physiological state. In this study, changes in blood lipid composition and levels of lipoproteins were determined after the injection of heparin in human. The level of LPL in plasma was increased from 0 to 11 mU/ml within 30-40 min post-heparin administration and decreased to the basal level within 2 h. The level of TGL in plasma decreased from 70 mg/dl to 20 mg/dl within 1 h and gradually increased to 80 mg/dl within 4 h. However the level of total cholesterol in plasma remained at 140 mg/dl during an experimental period of 4 h. Analysis of Lipoproteins in plasma by NaBr density gradient ultracentrifugation showed that the level of VLDL decreased from 50 mg/dl to 10 mg/dl within 1-2 h and returned to normal plasm level at 4 h. However there were no significant changes in the level of LDL and HDL. These results suggest that, at least, in normo-lipidemic subjects, increased free plasm LPL acts primarily on VLDL and failed to show any significant uptake of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins in human.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, JY., Kim, TK., Koo, BS. et al. Change of plasma lipoproteins by heparin-released lipoprotein lipase. Exp Mol Med 31, 60–64 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1999.10
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.1999.10
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lipoprotein concentration in patients requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Scientific Reports (2021)