Abstract
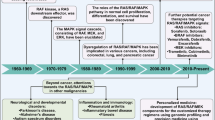
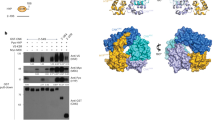
The ras, is a G-like protein that controls the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway involved in control and differentiation of cell growth. MAPK is a key component of its signaling pathway and the aberrant activation may play an important role in the transformation process. To better understand roles of ras in the activation of MAPKs, we have established ras transformed NIH3T3 fibroblast cell line, and analyzed the MAPK module. The ras transformed cells formed numerous spikes at the edges of cells and showed loss of contact inhibition. The levels of ERK1/2 MAPKs as revealed by Western blot analysis were not significantly different between ras transformed and non-transformed cells. However, phosphorylation of ERK MAPKs and the level of MEK were significantly increased although the heavily expressed level of Raf-1, an upstream component of MAPK pathway was unchanged in ras transformed NIH3T3 cells. The sedimentation profile of the MAPK module kinases in a glycerol gradient showed the presence of a rather homogeneous species of multimeric forms of ERK1/2 and MEK as indicated by the narrow distribution peak areas. The broad sedimentation profile of the Raf-1 in a glycerol gradient may suggest possible heterologous protein complexes but the identification of interacting molecules still remains to be identified in order to understand the organization of the MAPK signal transduction pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, KS., Kim, JA. & Chai, KJ. Molecular assembly of mitogen-activated protein kinase module in ras-transformed NIH3T3 cell line. Exp Mol Med 32, 120–126 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2000.21
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2000.21