Abstract
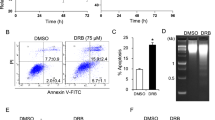
3-Deazaadenosine (DZA), one of the potent inhibitors of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, is known to possess several biological properties including an induction of apoptosis. To evaluate a possibility that DZA may be utilized for the treatment of human leukemia, we studied molecular events of cell death induced by DZA in human leukemia HL-60 and U-937 cells. DZA induced a specific cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and an activation of the cysteine protease caspase-3/CPP32 which is known to cleave PARP. DZA-mediated nuclear DNA-fragmentation was completely blocked in the presence of a universal inhibitor of caspases (z-VAD-fmk) or the specific inhibitor of caspase-3 (z-DEVD-fmk) unlike of cycloheximide (CHX). DNA fragmentation was preceded by the lowering of c-myc mRNA in the DZA treated cells. In addition, DZA-induced apoptosis was blocked by pretreatment with adenosine transporter inhibitors such as nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBTI) and dipyridamole (DPD). Taken together, these results demonstrate that DZA-induced apoptosis initiated through an active transport of DZA into human leukemia cells, is dependent on the caspase-3-like activity without de novo synthesis of proteins and possibly involves c-myc down-regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HS., Jeong, SY., Lee, JH. et al. Induction of apoptosis in human leukemia cells by 3-deazaadenosine is mediated by caspase-3-like activity. Exp Mol Med 32, 197–203 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2000.32
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2000.32
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apoptosis Inhibition Can Be Threatening in Aβ-Induced Neuroinflammation, Through Promoting Cell Proliferation
Neurochemical Research (2011)
-
Determination of caspase-3 activation fails to predict chemosensitivity in primary acute myeloid leukemia blasts
BMC Cancer (2005)
-
Analysis of the autoantibody repertoire in Burkitt?s lymphoma patients: frequent response against the transcription factor ATF-2
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2004)