Abstract
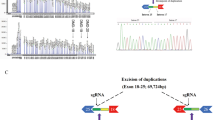
Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (D/BMD) are caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene. Two-thirds of patients have large intragenic deletions or duplications and the remaining one-third have point mutations, small deletions or insertions. Point mutations are more difficult to detect due to the enormous size (2.4 Mb) of the gene and its large transcript (14 kb). In the present study, a total of 50 DNA samples from unrelated D/BMD (38 DMD and 12 BMD) patients who did not show intragenic deletions by multiplex PCR, were analyzed for detection of point mutations. Single stranded conformation analysis and heteroduplex analysis observed electrophoretic mobility shifts in one (BMD) and two (DMD and BMD) patients, respectively. The mobility shift and heteroduplexes were observed in exon 17 in all of the three patients. Sequencing of the amplified PCR products revealed a nucleotide change (-37 g to t) in the intronic region in two of the patients while a C2268T substitution in the exonic region in one. Mutation database search for D/BMD mutations showed the nucleotide substitution in the exonic region as a novel change in the human dystrophin gene, which was not reported earlier. It resulted in an amino acid transition from threonine to methionine in the 687th position of the dystrophin protein. This novel substitution has been included in the mutation database of Leiden muscular dystrophy pages (http://www.dmd.nl) in the rare polymorphism/mutation category. The substituted nucleotide segregated with the disease phenotype in the family suggesting that it can be directly used for carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis without identification of disease causing mutation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaturvedi, L., Mukherjee, M., Srivastava, S. et al. Point mutation and polymorphism in Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophy (D/BMD) patients. Exp Mol Med 33, 251–256 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2001.41
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2001.41