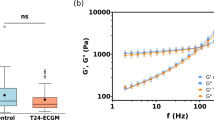
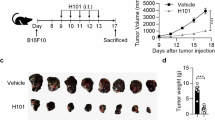
Abstract
Cell motility is essential for a wide range of cellular activities including anigogenesis as well as metastasis of tumor cells. Ras has been implicated in cell migration and invasion, and functions at upstream of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) families, which include extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK. In the present study, we examined the role of JNK in endothelial cell motility using stable transfectant (DAR-ECV) of ECV304 endothelial cells expressing previously established oncogenic H-Ras (leu 61). DAR-ECV cells showed an enhanced angiogenic potential and motility (∼2-fold) compared to ECV304 cells. Western blot analysis revealed constitutive activation of JNK in DAR-ECV cells. Pretreatment of JNK specific inhibitors, curcumin and all trans-retinoic acid, decreased the basal motility of DAR-ECV cells in a dose-dependent manner. These inhibitors also suppressed the motility stimulated by known JNK agonists such as TNFα and anisomycin. To further confirm the role of JNK, ECV304 cells expressing dominant active SEK1 (DAS-ECV) were generated. Basal non-stimulated levels of the cellular migration were greater in DAS-ECV clones than those in control ECV304 cells. These results suggest that Ras-SEK1-JNK pathway regulates motility of endothelial cells during angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others

Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, EY., Kim, SY. & Kim, EG. c-Jun N-terminal kinase is involved in motility of endothelial cell. Exp Mol Med 33, 276–283 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2001.45
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2001.45
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of JNK1 expression decreases migration and invasion of mouse hepatocellular carcinoma cell line in vitro
Medical Oncology (2011)
-
Elevated dietary linoleic acid increases gastric carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis in mice
British Journal of Cancer (2010)
-
H-ras transformation sensitizes volume-activated anion channels and increases migratory activity of NIH3T3 fibroblasts
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2008)
-
MKK signaling and vascularization
Oncogene (2007)
-
Interleukin-1β stimulates IL-8 expression through MAP kinase and ROS signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells
Oncogene (2004)