Abstract
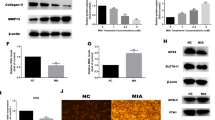
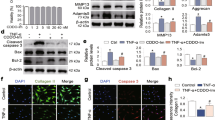
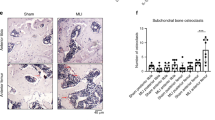
Nitric oxide (NO) has been considered as an important mediator in inflammatory phases and in loss of cartilage. In inflammatory arthritis, NO levels are correlated with disease activity and articular cartilage is able to produce large amounts of NO with the appropriate inducing factor such as cytokines. The old animals are shown to have a greater sensitivity to NO than young animals. This study evaluated the basal production of NO in normal and OA-affected chondroyctes from young and old patients and compared the levels of NO formation in response to IL-1β. The results showed that the basal levels were 7-fold higher in old chondrocytes than those of young cells. However, the IL-1β induced NO production was seen to decrease with age. Aminoguianidine (AG), a competitive inhibitor of iNOS, inhibited NO formation completely in both chondrocytes from young and old individuals. However, at the same concentration of AG it caused partial inhibition of NO and iNOS formation in chondrocytes from OA-affected individuals. In addition, although the IL-1β induced NO production was much lesser than that of young chondrocytes, the inhibition of collagen production by IL-1β was prominent in old chondrocytes and OA-affected chondrocytes. These results suggest that age-related differences in the regulation of NO production and collagen production, which may affect the ageing cells and osteoarthritic changes in some way.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Min, BH., Kim, H., Lim, H. et al. Effects of ageing and arthritic disease on nitric oxide production by human articular chondrocytes. Exp Mol Med 33, 299–302 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2001.48
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2001.48
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effects of PDTC on interleukin-1β-induced nitric oxide production in chondrocytes
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2009)