Abstract
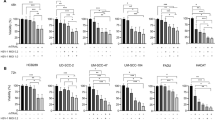
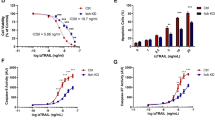
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), a member of the TNF family, selectively induce apoptosis in various transformed cell lines but not in almost-normal tissues. It is regulated by 2 death receptors, TRAIL receptor 1(TRAIL-R1) and TRAIL-R2 and 2 decoy receptors, TRAIL-R3 and TRAIL-R4. However, the determining factors of the sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis are not clearly understood. Herein, we investigated the expression of TRAIL-R, c-FLIP, FADD-like interleukin-1β-converting enzyme inhibitory protein, and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines. Seven of ten HCC cell lines showed resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis and five of seven TRAIL-resistant cell lines became sensitive to TRAIL by co-treatment with cycloheximide. In HCC cell lines, their TRAIL resistance did not correlate with the basal expression level of TRAIL receptors or c-FLIP, however, in human tissues, TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 expressions were notably decreased compared to normal counterpart. Cisplatin showed synergistic effect on TRAIL-induced apoptosis in most HCC cell lines regardless of their p53 status and TRAIL-R1 was induced by cisplatin treatment in certain cell lines. Inhibition of nuclear factor K B (NF-κB) by SN50, a peptide inhibitor of NF-κB activity, had no effect on TRAIL-induced apoptosis in HCC cells. These results suggest that (a) the majority of human HCC cell lines are resistant to TRAIL-induced apoptosis and cycloheximide-sensitive short-lived antiapoptotic molecule(s) is responsible for this resistance, (b) the expression of TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 is reduced in HCC tissues, and the increased expression of TRAIL-R1 may be a mechanism of cisplatininduced sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in some HCC cells, and (c) the activation of NF-κB may not be involved in the TRAIL resistance of HCC cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, EC., Seong, Y., Kim, C. et al. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells resist to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, and the resistance is abolished by cisplatin. Exp Mol Med 34, 114–122 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.17
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.17
This article is cited by
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma: targeting of oncogenic signaling networks in TRAIL resistant cancer cells
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Hepatitis B virus core protein inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis of hepatocytes by blocking DR5 expression
Cell Death & Differentiation (2009)
-
TRAIL is a key target in S-phase slowing-dependent apoptosis induced by interferon-β in cervical carcinoma cells
Oncogene (2005)