Abstract
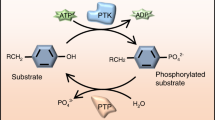
Protein-tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) constitute a family of receptor-like, and cytoplasmic enzymes, which catalyze the dephosphorylation of phosphotyrosine residues in a variety of receptors and signaling molecules. Together with protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs), PTPs are critically involved in regulating many cellular signaling processes. In this study, diverse compounds were screened for PTP inhibition and selectively screened for inhibitors with the end product inhibition properties. Among phosphate analogues and their derivatives for PTP inhibition, Keggin compounds phosphomolybdate (PM) and phosphotungstate (PT) strongly inhibited both PTP-1B and SHP-1, with K(i) values of 0.06-1.2 µM in the presence of EDTA. Unlike the vanadium compounds, inhibition potencies of PM and PT were not significantly affected by EDTA. PM and PT were potent, competitive inhibitors for PTPs, but relatively poor inhibitors of Ser/Thr phosphatase. Interestingly, PM and PT did not inhibit alkaline phosphatase at all. The crystal structure of PTP-1B in complex with PM, at 2.0 A resolution, reveals that MoO(3), derived from PM by hydrolysis, binds at the active site. The molybdenium atom of the inhibitor is coordinated with six ligands: three oxo-ligands, two apical water molecules and a S atom of the catalytic cysteine residue. In support of the crystallographic finding, we observed that molybdenium oxides (MoO(3), MoO(2), and MoO(2)Cl(2)) inhibited PTP-1B with IC(50) in the range 5-15 µM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Heo, YS., Ryu, J., Park, S. et al. Structural basis for inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases by Keggin compounds phosphomolybdate and phosphotungstate. Exp Mol Med 34, 211–223 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.30
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.30
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The interactions of metal cations and oxyanions with protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
BioMetals (2017)
-
Kinetics of Inhibition of Rabbit Intestine Alkaline Phosphatase by Heteroligand Peroxo Complexes of Vanadium(V) and Tungsten(VI)
Biological Trace Element Research (2009)
-
New peroxovanadium compounds containing biogenic co-ligands: synthesis, stability and effect on alkaline phosphatase activity
Transition Metal Chemistry (2008)
-
New oxo-bridged peroxotungsten complexes containing biogenic co-ligand as potent inhibitors of alkaline phosphatase activity
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2006)