Abstract
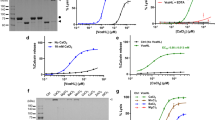
Vibrio vulnificus cytolysin (VVC) has been implicated as one of the important virulence determinants of V. vulnificus that causes serious septicemia and wound infection. An attempt was made to investigate that VVC could act as a ligand which stimulates intracellular signaling systems. Cholesterol dose-dependently blocked VVC hemolytic activity through oli-gomerization of cytolysin. Among cholesterol derivatives including 7-dehydrocholesterol, cholesteryl esters, deoxycholate, and cholestane tested, only 7-dehydrocholesterol induced oligomerization as well as inactivation of VVC. These results show that oligomerization of VVC is completely dependent on three-dimensional structure of cholesterol where specific interaction of cholesterol at oligomerization sites of VVC is very selective. These findings support the idea that cholesterol which constitute many of cellular plasma membrane could be a receptor of VVC on plasma membrane of target cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, BS., Kim, JS. Cholesterol induce oligomerization of Vibrio vulnificus cytolysin specifically. Exp Mol Med 34, 239–242 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.33
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.33
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vibiro vulnificus hemolysin associates with gangliosides
BMC Microbiology (2020)
-
The role of Vibrio vulnificus virulence factors and regulators in its infection-induced sepsis
Folia Microbiologica (2020)
-
Low density lipoprotein inactivates Vibrio vulnificus cytolysin through the oligomerization of toxin monomer
Medical Microbiology and Immunology (2005)