Abstract
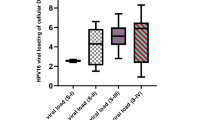
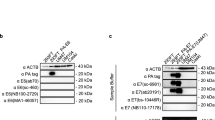
Human papillomavirus E7 (HPV E7) is a viral oncoprotein that plays an important role in cervical carcinogenesis through binding with retinoblastoma protein (Rb). Inactivation of Rb by E7 is necessary but not sufficient for cellular transformation, suggesting other protein-protein interactions are required for E7-mediated cellular transformation aside from the interaction with Rb. However, studies on the oncogenic function of HPV E7 have been limited by its poor immunoreactivity. In this report, we show that the fixation of purified recombinant HPV E7 on blotted nitrocellulose membrane with glutaldehyde markedly enhanced the immunoreactivity of HPV E7 protein. Using HeLa and Caski cell line which are infected with HPV 18 and HPV 16, respectively, we demonstrated that native HPV E7 proteins also could be detected by this method. These results therefore can provide the experimental conditions for detection of HPV E7 proteins with greater sensitivity and may help to analyze E7 functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, JH., Cho, SY., Kim, CW. et al. Improved immunodetection of human papillomavirus E7. Exp Mol Med 34, 496–499 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.69
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.69