Abstract
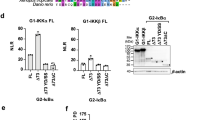
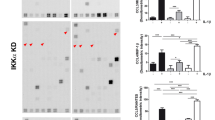
Antirheumatic gold compounds have been shown to inhibit NF-κB activation by blocking IκB kinase (IKK) activity. To examine the possible inhibitory mechanism of gold compounds, we expressed wild type and mutant forms of IKKα and β subunits in COS-7 cells and determined the effect of gold on the activity of these enzymes both in vivo and in vitro. Substitution of Cys-179 of IKKβ with alanine (C179A) rendered the enzyme to become resistant to inhibition by a gold compound auranofin, however, similar protective effect was not observed with an equivalent level of IKKα (C178A) mutant expressed in the cells. Auranofin inhibited constitutively active IKKα and β and variants; IKKα (S176E, S180E) or IKKβ (S177E, S181E), suggesting that gold directly cause inhibition of activated enzyme. The different inhibitory effect of auranofin on IKKα (C178A) and IKKβ (C179A) mutants indicates that gold could inhibit the two subunits of IKK in a different mode, and the inhibition of NF-κB and IKK activation induced by inflammatory signals in gold-treated cells appears through its interaction with Cys-179 of IKKβ.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, KI., Byun, MS. & Jue, DM. Gold compound auranofin inhibits IκB kinase (IKK) by modifying Cys-179 of IKKβ subunit. Exp Mol Med 35, 61–66 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2003.9
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2003.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dual inhibition of thioredoxin reductase and proteasome is required for auranofin-induced paraptosis in breast cancer cells
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
The effects of two gold-N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes in ovarian cancer cells: a redox proteomic study
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2022)
-
Phytochemicals as potential IKK-β inhibitor for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases in plant preservation: terpenoids, alkaloids, and quinones
Inflammopharmacology (2020)
-
Therapeutic effect of gold nanoparticles on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice with reference to interleukin-17 expression
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Intrinsic Effects of Gold Nanoparticles on Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Cortical Neurons
Neurochemical Research (2019)