Abstract
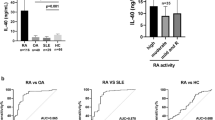
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease whose etiopathogenesis is not well understood. Although soluble (s) forms of 4-1BB (s4-1BB) and 4-1BB legand (s4-1BBL) have been detected in the sera of RA patients, their significance is not known. We compared the serum levels of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL in RA patients with those in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Behcet's disease (BD) patients. Serum levels of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL were significantly higher in RA patients compared with healthy controls, SLE or BD patients, and the abundance was correlated with disease severity in patients with RA. The serum levels of s4-1BB in RA patients were inversely corroborated with 4-1BB expression levels on activated T lymphocytes. In addition, there was a correlation between serum levels of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL. The augmented secretion of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL levels into the serum may reflect the clinical symptoms of RA and levels of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL in sera at the time of diagnosis may be indicative of the severity and outcome of RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, H., Choi, S., Choi, J. et al. Serum concentrations of soluble 4-1BB and 4-1BB ligand correlated with the disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med 36, 13–22 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.2
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
LIGHT regulated gene expression in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
Activation of 4-1BB signaling in bone marrow stromal cells triggers bone loss via the p-38 MAPK-DKK1 axis in aged mice
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Fish TNF and TNF receptors
Science China Life Sciences (2021)
-
Soluble immune checkpoints in cancer: production, function and biological significance
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2018)
-
Beyond TNF: TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2017)