Abstract
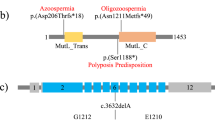
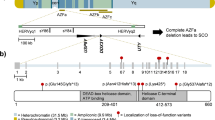
Our aim was to apply DNA chip technology as a diagnostic tool in infertility research and clinics. Six loci, including a sex-determining region on the Y chromosome and five sequence-tagged sites in azoospermia-factor regions were investigated in infertile male patients. Our method produced a sensitive signal, which showed the presence or absence of the STS regions on the Y chromosome. The results from 93 patients with non- obstructive azoospermia, oligoathenoteratozoospermia, or oligozoospermia were identical when analyzed with either the DNA chip technique or conventional PCR-gel electrophoresis. We have demonstrated its application in the molecular diagnosis of male infertility. This system provides an economic and high-throughput method for detecting the deletion of genomic DNA sequences of large groups of infertile patients, and a completely new approach to male infertility screening. The application of DNA chip technology to identify Yq deletions can also facilitate our understanding of male infertility.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Joo, H., Lee, SH. et al. Application of DNA chip techniques for Yq microdeletion analysis in infertile males. Exp Mol Med 36, 179–184 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.25
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.25