Abstract
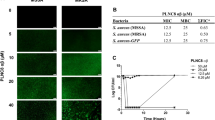
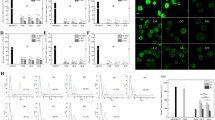
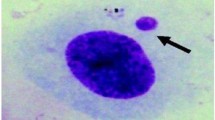
Mammalian epithelia produce the various antimicrobial peptides against the bacterial or viral infection, thereby acting as the active immune modulators in the innate immunity. In this study, we examined the effects of the various proinflammatory cytokines or LPS on cell viability and antimicrobial β-defensin gene expressions in human corneal epithelial cells. Results showed that the cytokines or LPS did not exert severe cytotoxic effects on the cells, and that β-defensin 1 was constitutively expressed, while β-defensin 2 was specifically induced by IL-1β, supporting the idea that these cytokines or LPS involve the defense mechanism in the cornea. Furthermore, the reporter and gel shift assay to define the induction mechanism of β-defensin 2 by IL-1β demonstrated that the most proximal NF-kB site on the promoter region of β-defensin 2 was not critical for the process. Data obtained from the normal or patients with the varying ocular diseases showed that our in vitro results were relevant in the clinical settings. Our results clearly demonstrated that β-defensin 1 and 2 are important antimicrobial peptides in the corneal tissues, and that the mechanistic induction process of β-defensin 2 by IL-1β is not solely dependent on proximal NF-kB site activation, thus suggesting that the long distal portion of the promoter is needed for the full responsiveness toward IL-1β.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, JS., Kim, CW., Kwon, YS. et al. Human β-defensin 2 is induced by interleukin-1b in the corneal epithelial cells. Exp Mol Med 36, 204–210 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.28
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.28
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lacritin Salvages Human Corneal Epithelial Cells from Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cell Death
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Signalling pathways involved in ribonuclease-7 expression
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2011)
-
Role of host-defence peptides in eye diseases
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2011)
-
Roles of human β-defensins in innate immune defense at the ocular surface: arming and alarming corneal and conjunctival epithelial cells
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2010)
-
Defensin and chemokine expression patterns in the palatine tonsil: a model of their local interaction
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (2006)