Abstract
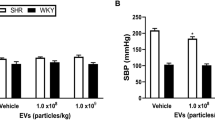
To evaluate the feasibility of treating hypertension by human tissue kallikrein gene (KLK1) delivery and by enzyme (rK1) administration, two recombinant vectors expressing KLK1 cDNA were constructed for gene delivery (pcDNA-KLK1) and recombinant enzyme preparation (pOV-KLK1). Expression of the pcDNA-KLK1 vector in COS-1 cells was confirmed by immunofluorescence and in spontaneous hypertension rats (SHR) by enzymatic detection. Following intramuscular or intravenous injection with the pcDNA-KLK1 vector, systolic pressure of SHR was significantly decreased, which lasted for 20 d to two months depending on dose, route and/or time of injection. Egg white containing recombinant hK1 was prepared by injection of egg-laying hens with the oviduct-specific expression vector pOV-KLK1 and administered into SHR via oral gavage. Following administration, systolic pressure of the SHR was decreased to that of normal rats, which lasted for 3-5 d depending on the dosage used. These data suggest that both hKLK1 gene delivery and recombinant enzyme administration can be used as alternative strategies for treating human hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Zhang, L., Wang, A. et al. Prolonged hypotensive effect of human tissue kallikrein gene delivery and recombinant enzyme administration in spontaneous hypertension rats. Exp Mol Med 36, 23–27 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.3
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.3