Abstract
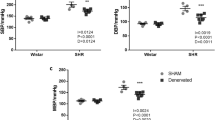
Hypertension and anemia may be causes of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in uremia but the molecular mechanism is not known. Uremia was induced in male Spraugue Dawley rats by 5/6 nephrectomy. The following groups of rats were studied for 6 weeks; uremic rats (U) fed ad. lib., control rats (C) pair-fed with U, U rats given hydralazine (100 mg/kg/day) (UH), U rats given erythropoietin (48U/kg/week, i.p.) (UE). Both diastolic and mean arterial pressures are higher (P<0.01) in U and UE compared with C whereas both pressures in UH were normalized. Hemoglobin in U was lower than in C, and was normalized in UE. U, UH and UE had higher heart weight/body weight ratios (HW/BW) as well as left ventricular weight/body weight ratios (LV/BW) compared with C (P<0.01). Compared with U, UH has lower HW/BW and LV/BW (P <0.05) and UE has normal HW/BW but lower LV/BW than U (P<0.05). To see if the gene expression in uremic LVH is similar to that described in pressure overload LVH in which mRNA levels of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), atrial natriuretic factors (ANF) and skeletal α-actin were increased, we measured these mRNA levels by Northern analysis. TGF-β, ACE and α-actin mRNA levels were not changed in all 4 groups. ANF mRNA in U and UE was increased 3 fold over C, and normalized in UH. Treatment of anemia with erythropoietin improved uremic LVH but did not change ANF mRNA; whereas treatment of hypertension with hydralazine normalized ANF mRNA but did not completely correct uremic LVH. Thus, gene expression in uremic LVH is distinct from that in pressure- overload LVH, suggesting that other unidentified factor(s) might be involved in uremic LVH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Mak, R., Chang, S., Draksharapu, A. et al. Gene expression in uremic left ventricular hypertrophy: effects of hypertension and anemia. Exp Mol Med 36, 251–258 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.34
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.34