Abstract
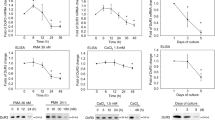
Epidermal keratinocyte differentiation is a tightly regulated stepwise process that requires protein kinase C (PKC) activation. Studies on cultured mouse keraitnocytes induced to differentiate with Ca2+ have indirectly implicated the involvement of PKCα isoform. When PKCα was overexpressed in undifferentiated keratinocytes using adenoviral system, expressions of differentiation markers such as loricrin, filaggrin, keratin 1 (MK1) and keratin 10 (MK10) were increased, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation was concurrently induced without change of other MAPK such as p38 MAPK and JNK1/2. Similarly, transfection of PKCα kinase active mutant (PKCα- CAT) in the undifferentiated keratinocyte, but not PKCβ-CAT, also increased differentiation marker expressions. On the other hand, PKCα dominant negative mutant (PKCβ-KR) reduced Ca2+ -mediated differentiation marker expressions, while PKCβ-KR did not, suggesting that PKCα is responsible for keratinocyte differentiation. When downstream pathway of PKCα in Ca2+ - mediated differentiation was examined, ERK1/2, p38 MAPK and JNK1/2 phosphorylations were increased by Ca2+ shift. Treatment of keratinocytes with PD98059, MEK inhibitor, and SB20358, p38 MAPK inhibitor, before Ca2+ shift induced morphological changes and reduced expressions of differentiation markers, but treatment with SP60012, JNK1/2 inhibitor, did not change at all. Dominant negative mutants of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK also inhibited the expressions of differentiation marker expressions in Ca2+ shifted cells. The above results indicate that both ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK may be involved in Ca2+- mediated differentiation, and that only ERK1/2 pathway is specific for PKCa-mediated differentiation in mouse keratinocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, H., Kwan, YW., Cho, CK. et al. PKCα induces differentiation through ERK1/2 phosphorylation in mouse keratinocytes. Exp Mol Med 36, 292–299 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.40
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Decoy receptor 3 is involved in epidermal keratinocyte commitment to terminal differentiation via EGFR and PKC activation
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
ADAM17/EGFR axis promotes transglutaminase-dependent skin barrier formation through phospholipase C γ1 and protein kinase C pathways
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Protective Effect of Phosphatidylcholine on Restoration of Ethanol-Injured Hepatocytes Related with Caveolin-1
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2014)
-
Role for Protein Kinase C-α in Keratinocyte Growth Arrest
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2009)
-
Functional Expression of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Human Differentiated Epidermis and Its Regulation by Cytokines
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2009)