Abstract
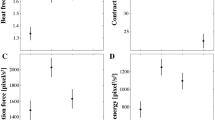
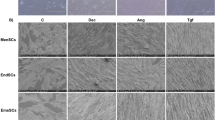
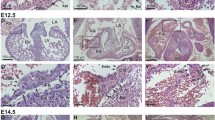
The P19 embryonal carcinoma cell line is a useful model cells for studies on cardiac differentiation. However, its low efficacy of differentiation hampers its usefulness. We investigated the effect of 5-azacytidine (5-aza) on P19 cells to differentiate into a high-efficacy cardiomyocytes. Embryoid-body-like structures were formed after 6 days with 1 µM of 5-aza in a P19 cell monolayer culture, beating cell clusters first observed on day 12, and, the production of beating cell clusters increased by 80.1% (29 of 36-wells) after 18 days. In comparison, the spontaneous beating cells was 33.3% (12 of 36-wells) for the untreated control cells. In response to 1 µM of 5-aza, P19 cells expressed bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), BMP-4, Bmpr1a and Smad1 at day 6 or 9, and also cardiac markers such as GATA-4, Nkx2.5, cardiac troponin I, and desmin were up-regulated in a time-dependent manner after induction of BMP signaling molecules. Immunocytochemistry revealed the expression of smooth muscle a-actin, sarcomeric a-actinin, cardiac myosin heavy chain, cardiac troponin T and desmin, respectively. The proportion of sarcomeric a-actinin positive cells accounted for 6.48% on day 15 after 5-aza exposure as measured by flow cytometry. This study has demonstrated that 5-aza induces differentiation of P19 cells into cardiomyocytes in a confluent monolayer culture in the absence of prior embryoid formation and dimethyl sulfoxide exposure, depending in part on alteration of BMP signaling molecules. These results suggest that 5-aza treatment could be used as a new method for cardiac differentiation in P19 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, SC., Yoon, J., Shim, WJ. et al. 5-azacytidine induces cardiac differentiation of P19 embryonic stem cells. Exp Mol Med 36, 515–523 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.66
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.66
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Human cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes induce cardiac gene expressions in mesenchymal stromal cells within 3D hyaluronic acid hydrogels and in dose-dependent manner
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine (2021)
-
Small molecule 2′-deoxycytidine differentiates human umbilical cord-derived MSCs into cardiac progenitors in vitro and their in vivo xeno-transplantation improves cardiac function
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2020)
-
A potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of sirtuin 1 promotes differentiation of pluripotent P19 cells into functional neurons
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Zebularine regulates early stages of mESC differentiation: effect on cardiac commitment
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
Direct comparison of distinct cardiomyogenic induction methodologies in human cardiac-derived c-kit positive progenitor cells
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2012)