Abstract
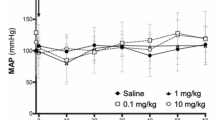
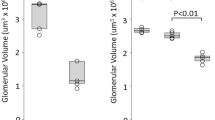
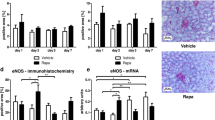
VEGF expressed in glomerular podocytes, is known to increase vascular permeability to macromolecules. Angiotensin II can stimulate the release of VEGF, and the protective effects of angiotensin II antagonist against diabetic glomerular injury suggest that the angiotensin II-induced VEGF is an important pathogenetic mechanism in the development of proteinuria during diabetic nephropathy although this mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, the changes of VEGF expression was examined in the experimental diabetic nephropathy to determine whether these changes were modified by renoprotective intervention by blockers of angiotensin II receptors. The streptozotocin- induced diabetic rats were treated with L-158,809, a blocker of angiotensin II receptors, for 12 weeks. Age-matched rats with L-158,809 served as controls. RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry were used to assess and quantify gene and protein expression of VEGF. A progressive increase in urinary protein excretion was observed in diabetic rats. Glomerular VEGF expression was significantly higher in diabetic rats than in the control groups, with a significant reduction in glomerular VEGF expression and proteinuria in L-158,809- treated diabetic rats. VEGF mRNA was also significantly higher in diabetic kidneys than in the control groups, with a significant reduction in VEGF mRNA in L-158,809-treated diabetic kidneys. These results demonstrates that VEGF expression is significantly increased in diabetic podocytes, and angiotensin II receptor antagonist attenuated these changes in VEGF expression and prevented the development of proteinuria in vivo. Attenuation of increased VEGF expression in podocytes could contribute to the renoprotective effects of angiotensin II receptor antagonists in diabetic nephropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, EY., Shim, M., Kim, M. et al. Angiotensin II receptor blocker attenuates overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor in diabetic podocytes. Exp Mol Med 36, 65–70 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.9
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2004.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The protective effect of the RAS inhibitor on diabetic patients with nephropathy in the context of VEGF suppression
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2009)
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor and diabetic nephropathy
Current Diabetes Reports (2008)
-
Antiproteinuric effect of RAS blockade: New mechanisms
Current Hypertension Reports (2004)