Abstract
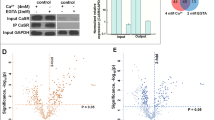
The calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) plays an important role for sensing local changes in the extracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]o) in bone remodeling. Although the function of CaSR is known, the regulatory mechanism of CaSR remains controversial. We report here the regulatory effect of caveolin on CaSR function as a process of CaSR regulation by using the human osteosarcoma cell line (Saos-2). The intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) was increased by an increment of [Ca2+]o. This [Ca2+]i increment was inhibited by the pretreatment with NPS 2390, an antagonist of CaSR. RT-PCR and Western blot analysis of Saos-2 cells revealed the presence of CaSR, caveolin (Cav)-1 and -2 in both mRNA and protein expressions, but there was no expression of Cav-3 mRNA and protein in the cells. In the isolated caveolae-rich membrane fraction from Saos-2 cells, the CaSR, Cav-1 and Cav-2 proteins were localized in same fractions (fraction number 4 and 5). The immuno-precipitation experiment using the respective antibodies showed complex formation between the CaSR and Cav-1, but no complex formation of CaSR and Cav-2. Confocal microscopy also supported the co-localization of CaSR and Cav-1 at the plasma membrane. Functionally, the [Ca2+]o- induced [Ca2+]i increment was attenuated by the introduction of Cav-1 antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN). From these results, in Saos-2 cells, the function of CaSR might be regulated by binding with Cav-1. Considering the decrement of CaSR activity by antisense ODN, Cav-1 up-regulates the function of CaSR under normal physiological conditions, and it may play an important role in the diverse pathophysiological processes of bone remodeling or in the CaSR- related disorders in the body.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, S., Kwak, JO., Kim, HW. et al. Calcium sensing receptor forms complex with and is up-regulated by caveolin-1 in cultured human osteosarcoma (Saos-2) cells. Exp Mol Med 37, 91–100 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.13
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.13
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Key mRNAs and lncRNAs in Osteosarcoma Response to Preoperative Chemotherapy with Prognostic Values
Current Medical Science (2021)
-
Regulation of CYP27B1 mRNA Expression in Primary Human Osteoblasts
Calcified Tissue International (2016)
-
Expression of Caveolin-1 in Periodontal Tissue and Its Role in Osteoblastic and Cementoblastic Differentiation In Vitro
Calcified Tissue International (2016)
-
The calcium sensing receptor: from calcium sensing to signaling
Science China Life Sciences (2015)
-
A novel CASR mutation in a Tunisian FHH/NSHPT family associated with a mental retardation
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)