Abstract
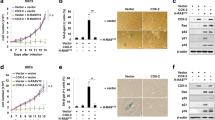
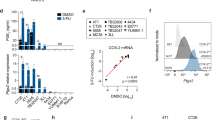
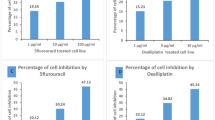
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) has been reported to be associated with tumor development and progression as well as to protect cells from apoptosis induced by various cellular stresses. Through a tetracycline-regulated COX-2 overexpression system, we found that COX-2 inhibits detachment-induced apoptosis (anoikis) in a human bladder cancer cell line, EJ. We also found that the inhibition of anoikis by COX-2 results from activation of the PI-3K/Akt pathway as evidenced by suppression of the COX-2 effect on anoikis by a PI-3K inhibitor, LY294002. Furthermore, COX-2 enhanced Mcl-1 expression in the anoikis process, implying that Mcl-1 also may be involved in mediating the survival function of COX-2. Together, these results suggest that COX-2 inhibits anoikis by activation of the PI-3K/Akt pathway and probably by enhancement of Mcl-1 expression in human bladder cancer cells. This anti- anoikis effect of COX-2 may be a part of mechanisms to promote tumor development and progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, EM., Kwak, SJ., Kim, YM. et al. COX-2 inhibits anoikis by activation of the PI-3K/Akt pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Exp Mol Med 37, 199–203 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.27
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.27
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multi-cohort validation of Ascore: an anoikis-based prognostic signature for predicting disease progression and immunotherapy response in bladder cancer
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
Identification of novel COX-2 / CYP19A1 axis involved in the mesothelioma pathogenesis opens new therapeutic opportunities
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
Cross-talk between SIM2s and NFκB regulates cyclooxygenase 2 expression in breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research (2019)
-
The inhibitory effect of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS-398 on the cholangiocarcinoma line (QBC939)
The Chinese-German Journal of Clinical Oncology (2012)