Abstract
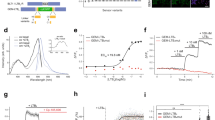
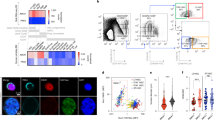
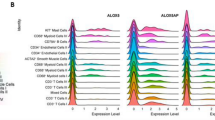
Leukotriene B4(LTB4), derived from arachidonic acid, is a potent chemotactic agent and activating factor for hematopoietic cells. In addition to host defense in vivo, several eicosanoids have been reported to be involved in stem cell differentiation or proliferation. In this study, we investigated the effect of LTB4 on human cord blood CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). LTB4 was shown to induce proliferation of HSC and exert anti-apoptotic effect on the stem cells. Blockade of interaction between LTB4 and its receptor enhanced self-renewal of the stem cells. Effect of LTB4 on differentiation of CD34+ HSCs were confirmed by clonogenic assays, and induction of the expression of BLT2 (the low- affinity LTB4 receptor), during the ex vivo expansion was confirmed by reverse transcription-PCR. Our results suggest that LTB4-BLT2 interaction is involved in the cytokine-induced differentiation and ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, J., Kim, GY., Mun, YC. et al. Leukotriene B4 pathway regulates the fate of the hematopoietic stem cells. Exp Mol Med 37, 45–50 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.6
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Eicosanoids and HB-EGF/EGFR in cancer
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2018)
-
Essential fatty acids and their metabolites as modulators of stem cell biology with reference to inflammation, cancer, and metastasis
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2011)
-
Eicosanoids and cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2010)
-
Eicosanoid regulation of hematopoiesis and hematopoietic stem and progenitor trafficking
Leukemia (2010)
-
BLT2 is expressed in PanINs, IPMNs, pancreatic cancer and stimulates tumour cell proliferation
British Journal of Cancer (2008)