Abstract
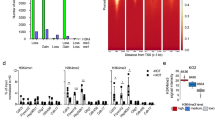
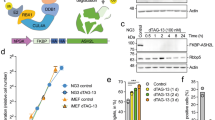
Calmegin is a testis-specific molecular chaperon playing a key role in spermatogenesis. However, the transcriptional regulatory mechanisms for calmegin expression are entirely unknown. Herein, we revealed that calmegin is transcriptionally regulated by histone deacetylase (HDAC) and CpG methyltransferase. The cDNA microarray analysis of the human fibrosarcoma cells treated with trichostatin A (TSA) showed an increased level of calmegin mRNA. The induction of calmegin mRNA by TSA was added by the treatment with 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5'Aza- dC), implying that epigenetic alterations are involved in the transcriptional repression of the gene. Moreover, chromatin immunoprecipitation assay using an anti-acetyl-histone H3 antibody exhibited that the proximal region (-152~-31) of the calmegin promoter is responsible for HDAC-mediated transcriptional repression of the gene. These results demonstrate that calmegin expression is regulated by HDAC and CpG methyltransferase in a coordinative way.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Shim, J. & Kwon, H. Coordinated transcriptional regulation of calmegin, a testis-specific molecular chaperon, by histone deacetylase and CpG methyltransferase. Exp Mol Med 37, 492–496 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.61
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.61
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Histone chaperones regulate histone exchange during transcription
The EMBO Journal (2007)