Abstract
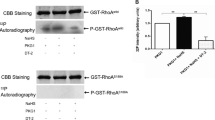
Rac1 and Rac2 are essential for the control of oxidative burst catalyzed by NADPH oxidase. It was also documented that Rho is associated with the superoxide burst reaction during phagocytosis of serum- (SOZ) and IgG-opsonized zymosan particles (IOZ). In this study, we attempted to reveal the signal pathway components in the superoxide formation regulated by Rho GTPase. Tat-C3 blocked superoxide production, suggesting that RhoA is essentially involved in superoxide formation during phagocytosis of SOZ. Conversely SOZ activated both RhoA and Rac1/2. Inhibition of RhoA-activated kinase (ROCK), an important downstream effector of RhoA, by Y27632 and myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) by ML-7 abrogated superoxide production by SOZ. Extracellular signaling-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) were activated during phagocytosis of SOZ, and Tat-C3 and SB203580 reduced ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation, suggesting that RhoA and p38 MAPK may be upstream regulators of ERK1/2. Inhibition of ERK1/2, p38 MAPK, phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase did not block translocation of RhoA to membranes, suggesting that RhoA is upstream to these kinases. Inhibition of RhoA by Tat-C3 blocked phosphorylation of p47 PHOX. Taken together, RhoA, ROCK, p38MAPK, ERK1/2, and p47 PHOX may be subsequently activated, leading to activation of NADPH oxidase to produce superoxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JS., Kim, JG., Jeon, CY. et al. Downstream components of RhoA required for signal pathway of superoxide formation during phagocytosis of serum opsonized zymosans in macrophages. Exp Mol Med 37, 575–587 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.71
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.71
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Macrophage-specific RhoA knockout delays Wallerian degeneration after peripheral nerve injury in mice
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2021)
-
Newborn sex-specific transcriptome signatures and gestational exposure to fine particles: findings from the ENVIRONAGE birth cohort
Environmental Health (2017)
-
Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitors Promote Microglial Uptake Via the ERK Signaling Pathway
Neuroscience Bulletin (2016)
-
Dexamethasone suppresses infiltration of RhoA+ cells into early lesions of rat traumatic brain injury
Acta Neuropathologica (2008)