Abstract
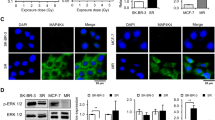
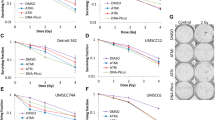
Here we determined which radiation-responsive genes were altered in radioresistant CEM/IR and FM3A/IR variants, which showed higher resistance to irradiation than parental human leukemia CEM and mouse mammary carcinoma FM3A cells, respectively and studied if radioresistance observed after radiotherapy could be restored by inhibition of protein kinase A. The expressions of DNA-PKcs, Ku70/80, Rad51 and Rad54 genes that related to DNA damage repair, and Bcl-2 and NF-κB genes that related to antiapoptosis, were up-regulated, but the expression of proapototic Bax gene was down-regulated in the radioresistant cells as compared to each parental counterpart. We also revealed that the combined treatment of radiation and the inhibitor of protein kinase A (PKA) to these radioresistant cells resulted in synergistic inhibition of DNA-PK, Rad51 and Bcl-2 expressions of the cells, and consequently restored radiosensitivity of the cells. Our results propose that combined treatment with radiotherapy and PKA inhibitor can be a novel therapeutic strategy to radioresistant cancers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, C., Bae, J., Kim, M. et al. Radiosensitization by targeting radioresistance-related genes with protein kinase A inhibitor in radioresistant cancer cells. Exp Mol Med 37, 608–618 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.74
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.74
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enhancement of radiosensitivity by a unique novel NF-κB inhibitor, DHMEQ, in prostate cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2012)
-
Alteration of apoptotic signaling molecules as a function of time after radiation in human neuroblastoma cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2008)