Abstract
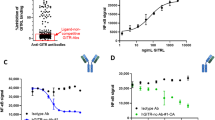
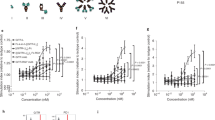
GITR (glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor) is a recently identified member of the TNF receptor superfamily. The receptor is preferentially expressed on CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells and GITR signals break the suppressive activity of the subset. In this study, we wanted to reveal the in vivo function of GITR in chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), a lupus-like autoimmune disease. A single injection of anti-GITR monoclonal antibody (DTA-1) was effective in blocking the progression of cGVHD in the parent-into-F1 model. Treatment of DTA-1 significantly decreased levels of IgG1 anti-DNA autoantibody, inhibited glomerulonephritis, and increased survival. The DTA-1-mediated inhibition of autoantibody production correlated with deletion of B cells and could occur independently of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Our results indicate that anti-GITR monoclonal antibody may be used as a potential immunotherapeutic agent for preventing cGVHD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Choi, W., Kim, H. et al. Prevention of chronic graft-versus-host disease by stimulation with glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Exp Mol Med 38, 94–99 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.11
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.11
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The pentapeptide PLNPK inhibits systemic lupus erythematosus-associated renal damage
Inflammation Research (2010)