Abstract
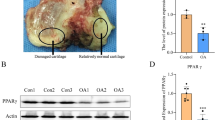
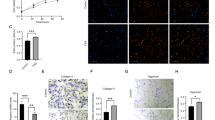
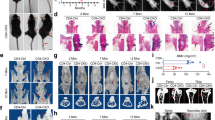
Although the apoptosis of chondrocytes plays an important role in endochondral ossification, its mechanism has not been elucidated. In this study, we show that guanosine induces chondrocyte apoptosis based on the results of acridine orange/ ethidium bromide staining, caspase-3 activation, and sub-G1 fraction analysis. The potent inhibitory effect of dipyridamole, a nucleoside transporter blocker, indicates that extracellular guanosine must enter the chondrocytes to induce apoptosis. We found that guanosine promotes Fas-Fas ligand interaction which, in turn, leads to chondrocyte apoptosis. These findings indicate a novel mechanism for endochondral ossification via metabolic regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DJ., Chung, JH., Ryu, EK. et al. Metabolic loading of guanosine induces chondrocyte apoptosis via the Fas pathway. Exp Mol Med 38, 401–407 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.47
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.47