Abstract
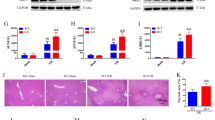
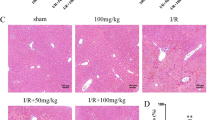
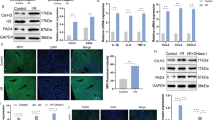
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is activated during hepatic reperfusion, and JNK inhibitors are known to protect other major organs from ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. We attempted to determine the effect of SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, on hepatic I/R injury using a partial ischemia model in mice. Compared to a vehicle-treated group, the SP600125-treated group showed a greater increase in serum ALT levels 24 h after reperfusion with more severe parenchymal destruction and leukocyte infiltration. Similarly, tissue myeloperoxidase and malondialdehyde levels were higher in the SP600125-treated group, and chemokine expression was also higher in the SP600125-treated group. These data, which are contradictory to previous results, indicate that JNK inhibition by SP600125 may be harmful in hepatic I/R injury. Therefore, care must be taken when investigating the therapeutic use of JNK inhibitors in hepatic I/R injury, especially in the context of the effects of JNK inhibition on inflammatory infiltration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KH., Kim, SE. & Lee, YS. SP600125, a selective JNK inhibitor, aggravates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Mol Med 38, 408–416 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.48
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.48
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of p38 and JNK in liver ischemia and reperfusion
Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery (2009)