Abstract
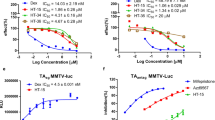
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are the most effective group of medications available to treat inflammation. Although most patients with inflammation respond to GC, a small group of patients exhibit persistent GC-resistance with prolonged inflammation. Previously, it was proposed that the GC-resistance is caused by low amount of human GC receptor (hGRα) and/or excessive presence of a GC receptor isoform, hGRβ that was generated from alternative splicing of the hGR message. We have tested this hypothesis by investigating correlation between the expression pattern of hGR mRNAs in patients with inflammatory nasal polyps and the effectiveness of GC treatment. We have performed reverse transcription PCR analysis of mRNAs coding each hGRα and hGRβ in nasal tissues. hGRα mRNA was more expressed in patients with nasal polyps than in normal subjects. However, the elevated hGRα mRNA expression was decreased after GC treatment. Compared with hGRα mRNA expression, level of hGRβ mRNA expression was very low in all groups. In patients, hGRβ mRNA was expressed at a similar level regardless of GC efficacy, indicating that there is no correlation between the GC sensitivity and the expression level of hGRβ mRNA. Thus, persistent GC-resistance is not associated with low expression of hGRa or over- expression of hGRβ.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, BR., Kwon, JH., Gong, SJ. et al. Expression of glucocorticoid receptor mRNAs in glucocorticoid-resistant nasal polyps. Exp Mol Med 38, 466–473 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.55
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.55
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of multiple isoforms of glucocorticoid receptor in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
Journal of Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery (2022)
-
Sinus computed tomography predicts clinical response to corticosteroids in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Clinical and Translational Allergy (2018)
-
Low expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha isoform in adult immune thrombocytopenia correlates with glucocorticoid resistance
Annals of Hematology (2013)