Abstract
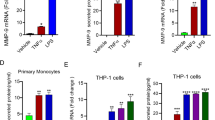
The migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) into the intima, an important step in injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia, requires the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and the consequent up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). This study was undertaken to test for a possible effect of α-lipoic acid (ALA), a potent inhibitor of NF-κB, on MMP-9 expression. ALA inhibited high-glucose- and TNF-α-stimulated VSMC migrations in vitro. It also inhibited high-glucose- and TNF-α-induced increases in MMP-9 expression. The activity of MMP-9-promoter constructs with mutations in the NF-κB binding site was not inhibited by ALA, indicating an involvement of the NF-κB signaling pathway in the ALA-specific inhibition of MMP-9. These data suggest the possibility that ALA may be useful for the prevention of neointimal hyperplasia after angioplasty, by inhibiting the NF-κB/ MMP-9 pathway, especially with hyperglycemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HS., Kim, HJ., Park, KG. et al. α-Lipoic acid inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by inhibiting NF-κB transcriptional activity. Exp Mol Med 39, 106–113 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.12
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lipoic acid. Kinetics and pluripotent biological properties and derivatives
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
The involvement of spinal annexin A10/NF-κB/MMP-9 pathway in the development of neuropathic pain in rats
BMC Neuroscience (2019)
-
Alpha-lipoic acid ameliorates the epithelial mesenchymal transition induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction in mice
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Lipoic acid plays a role in scleroderma: insights obtained from scleroderma dermal fibroblasts
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2014)
-
Adverse cardiac responses to alpha-lipoic acid in a rat-diabetic model: possible mechanisms?
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2013)