Abstract
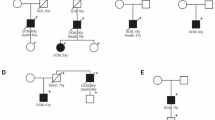
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is characterized by cardiac dilation and systolic dysfunction. So far sixteen genes have been shown to cause autosomal dominant familial dilated cardiomyopathy (FDC). We identified a large Korean family from the Jeju island showing a clear Mendelian inheritance of FDC. A genomewide linkage scan at 9 cM marker density identified a peak multipoint LOD score of 2.82 at D1S195. Haplotyping of the region with 15 additional markers defined a candidate interval that included a known candidate gene encoding the lamin A/C (LMNA). Sequencing of the LMNA exons revealed one missense mutation at C568T (Arg190Trp) in the α-helical rod domain of the LMNA gene cosegregating with FDC with conduction-system disease. The same mutation was found in patients of another Korean family with FDC without conduction-system disease. Upon screening 14 sporadic DCM cases, we found three LMNA mutations including a case having a previously described (Glu161Lys) mutation and two having novel mutations (Glu53Val and Glu186Lys). Our results suggest that variable genotypes of laminopathy are implicated in not only familial but also considerable proportion of sporadic DCM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, K., Dube, MP., Lim, J. et al. Lamin A/C mutations associated with familial and sporadic cases of dilated cardiomyopathy in Koreans. Exp Mol Med 39, 114–120 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.13
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.13
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Development of anthracycline-induced dilated cardiomyopathy due to mutation on LMNA gene in a breast cancer patient: a case report
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2019)
-
Identification of mutational hot spots in LMNA encoding lamin A/C in patients with familial dilated cardiomyopathy
Basic Research in Cardiology (2009)
-
Clinical utility of genetic tests for inherited hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies
Cardiovascular Ultrasound (2008)