Abstract
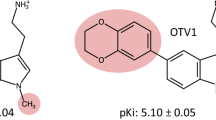
Serotonin receptor subtype 6 (5-HT(6)) is a neurotransmitter receptor, which is involved in various brain functions such as memory and mood. It mediates signaling via the interaction with a stimulatory G-protein. Especially, the third intracellular loop (iL3) of 5-HT(6) and the α subunit of stimulatory G protein (Gα(s)) are responsible for the signaling process of 5-HT(6). Chemical compounds that could inhibit the interaction between the iL3 region of 5-HT(6) and Gα(s) were screened from a chemical library consisted of 5,600 synthetic compounds. One of the identified compounds bound to Gα(s) and effectively blocked the interaction between Gα(s) and the iL3 region of 5-HT(6). The identified compound was further shown to reduce the serotonin-induced accumulation of cAMP in 293T cells transformed with 5-HT(6) cDNA. It also lowered the Ca2+ efflux induced by serotonin in cells expressing 5-HT(6) and chimeric Gα(s5/q). These results indicate that the interaction between the iL3 of 5-HT(6) and Gα(s) can be exploited for screening of regulatory compounds against the signaling pathway of 5-HT(6).
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Y., Kang, H., Lee, W. et al. An inhibitory compound against the interaction between Gα(s) and the third intracellular loop region of serotonin receptor subtype 6 (5-HT(6)) disrupts the signaling pathway of 5-HT(6). Exp Mol Med 39, 335–342 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.37
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.37
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Peptides Mimicking the Third Intracellular Loop of 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptors of the Types 1B and 6 Selectively Activate G Proteins and Receptor-Specifically Inhibit Serotonin Signaling via the Adenylyl Cyclase System
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2010)