Abstract
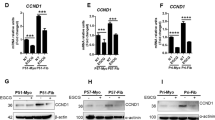
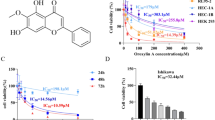
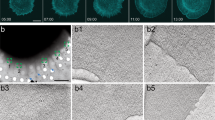
Axin is a negative regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and is involved in the regulation of axis formation and proliferation. Involvement of Axin in the regulation of other signaling pathways is poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the involvement of Akt in growth regulation by Axin in L929 fibroblasts stimulated by EGF. Akt activity was increased by EGF treatment and Ras activation, respectively. Both the EGF- and Ras-induced Akt activations were abolished by Axin induction, as revealed by both Western blot and immunocytochemical analyses. The proliferation and Akt activation induced by EGF were decreased by Axin induction, and the effects of EGF were abolished by treatment of an Akt-specific inhibitor. Therefore, Axin inhibits EGF-induced proliferation of L929 fibroblasts by blocking Akt activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, S., Jeong, WJ., Cho, JY. et al. Akt is involved in the inhibition of cell proliferation by EGF. Exp Mol Med 39, 491–498 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.54
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.54