Abstract
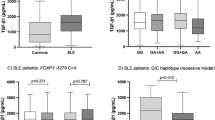
The forkhead-box J1 (FOXJ1) transcription factor could suppress a spontaneous activation of T cells and B cells through an induction of IκBβ that results in repression of NF-κB activity. In Foxj1 deficiency mice, systemic autoimmune inflammation is quite common symptom. Therefore, deregulated Foxj1 is supposed to be associated with autoimmune diseases and/or other inflammatory diseases. Previously, we identified that polymorphisms of human FOXJ1 gene (g.-460C>T, g.1805G>T and g.3375G>C) are associated with allergic rhinitis in a Korean population. In present study, we compared the genotype and allele frequencies of these SNPs between healthy controls and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. We also investigated the relationships between each genotype and the expression levels of anti-nuclear antibodies in SLE patients, and rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide in RA patients. The frequencies of haplotypes constructed by these FOXJ1 SNPs were compared between controls and SLE (or RA) patients. The results of genotype and allele analysis showed that the prevalence of polymorphism g.3375G>C was associated with the susceptibility of SLE (P = 0.0072 and 0.0042, respectively). But no significant association was found with RA. In the haplotype analysis, however, the main CGG showed a weak association between controls and RA patients (P = 0.048).
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CS., Zhang, Q., Lim, MK. et al. Association of FOXJ1 polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis in Korean population. Exp Mol Med 39, 805–811 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.87
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2007.87
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
EPSTI1 polymorphisms are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
Genes & Genomics (2017)
-
Gene expression profiling of human alveolar epithelial cells (A549 cells) exposed to atmospheric particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) collected from Seoul, Korea
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology (2014)
-
Polymorphisms of interleukin-31 are associated with anti-CCP levels in females with rheumatoid arthritis
Journal of Genetics (2014)
-
TSLPR gene polymorphism is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in the Korean population
Genes & Genomics (2012)