Summary
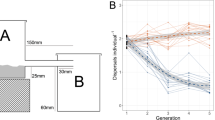
Replicated populations of the flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum, were reared under nine population structures consisting of combinations of three effective population sizes and three interdemic migration rates. For each treatment, the expected loss of genetic variance within demes owing to the cumulative effects of finite population size was calculated and related to observed changes in density-dependent population growth rates. A strong positive correlation was demonstrated between the predicted decline in within-deme genetic variance and the degree to which a deme's rate of increase declined over time. Notably, changes in the rate of population increase could be detected when the predicted loss in genetic variance was as low as 10 per cent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Birch, L C, Park, T, and Frank, M B. 1951. The effect of intraspecies and interspecies competition on the fecundity of two species of flour beetles. Ecology, 5, 116–132.
Crow, J F, and Kimura, M. 1970. An Introduction to Population Genetics Theory. Harper and Row, New York, New York.
Kence, A. 1973. The effects of variation in larval development on laboratory populations of Tribolium and houseflies. Ph.D thesis, State University of New York at Stony Brook, New York.
King, C E, and Dawson, P S. 1972. Population biology and the Tribolium model. Evol Biol, 5, 133–227.
Levene, H, Lerner, I M, Sokoloff, A, Ho, F K, and Franklin, I R. 1965. Genetic load in Tribolium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 53, 1042–1050.
Lopez-Fanjul, C, and Jodar, B. 1977. The genetic properties of egg laying of virgin females of Tribolium castaneum. Heredity, 39, 251–258.
McCauley, D E. 1978. Demographic and genetic responses of two strains of Tribolium castaneum to a novel environment. Evolution, 32, 398–415.
McCauley, D E, and Wade, M J. 1980. Group selection: the genetic and demographic basis for the phenotypic differentiation of small populations of Tribolium castaneum. Evolution, 34, 813–821.
Mertz, D B. 1972. The Tribolium model and the mathematics of population growth. Annu Rev Ecol Syst, 3, 51–78.
Mertz, D B, and Robertson, J R. 1970. Some developmental consequences of handling, egg-eating, and population density for flour beetle larvae. Ecology, 51, 989–998.
Osborne, J W. 1968. Inter-and intra-species copulation effect on net fecundity in Tribolium confusum. Trans Missouri Acad Sci, 2, 53–57.
Park, T. 1934. Studies in population physiology III. The effect of conditioned flour upon the productivity and population decline of Tribolium confusum. J Exp Zool, 68, 167–182.
Park, T. 1935. Studies in population physiology IV. Some physiological effects of conditioned flour upon Tribolium confusum Duval and its populations. Physiol Zool, 8, 91–115.
Park, T. 1938a. A note on the size and composition of old Tribolium confusum populations. Amer Natur, 72, 24–33.
Park, T. 1938b. Studies in population physiology VIII. The effect of larval population density on the post-embryonic development of the flour beetle, Tribolium confusum Duval. J Exp Zool, 79, 51–70.
Park, T, and Woollcott, N. 1937. Studies in population physiology VIII. The relation of environmental conditioning to the decline of Tribolium confusum populations. Physiol Zool, 10, 197–211.
Sokoloff, A. 1974. The Biology of Tribolium Vol. 2. Oxford University Press, London.
Sokoloff, A. 1977. The Biology of Tribolium Vol. 3. Oxford University Press, London.
Sonleitner, F J. 1961. Factors affecting egg cannibalism and fecundity in populations of adult Tribolium castaneum Herbst. Physiol Zool, 34, 233–255.
Wade, M J. 1977. An experimental study of group selection. Evolution, 31, 134–153.
Wade, M J. 1979. The primary characteristics of Tribolium populations group selected for increased and decreased population size. Evolution, 33, 749–764.
Wade, M J. 1980. Effective population size: the effects of sex, genotype, and density on the mean and variance of offspring numbers in the flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Genet Res, 36, 1–10.
Wade, M J, and McCauley, D E. 1980. Group selection: the phenotypic and genptypic differentiation of small populations. Evolution, 34, 799–812.
Wright, S. 1931. Evolution in Mendelian populations. Genetics, 16, 93–159.
Wright, S. 1977. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations: Vol III. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, Illinois.
Wright, S. 1978. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations: Vol IV. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, Illinois.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCauley, D., Wade, M. The populational effects of inbreeding in Tribolium. Heredity 46, 59–67 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1981.6
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1981.6
This article is cited by
-
Tribolium beetles as a model system in evolution and ecology
Heredity (2021)
-
Gene Flow and Adaptive Potential in Drosophila melanogaster
Conservation Genetics (2006)