Abstract
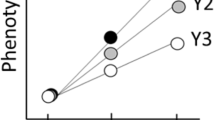
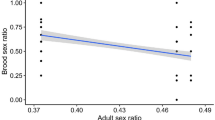
Sex ratio in Silene alba is generally female biased, and the bias is influenced by Y-linked alleles that are polymorphic in natural populations. One interpretation of these alleles is that they enhance the production of males in female-biased populations, i.e. they are restorers. Two Silene species, S. alba and S. dioica, and their reciprocal hybrids were used to investigate the inheritance of sex ratio and the relationship between sex ratio and male fertility. Sex ratio was paternally inherited (i.e. Y-linked), but was also strongly influenced by the maternal parent through an interaction with the Y chromosome. These results corroborate previous work on the inheritance of sex ratio within S. alba, and suggest that sex ratio in S. alba and S. dioica has a similar genetic basis. Examination of the maternal by Y chromosome interaction revealed that the Y chromosome of each species produced a more severe female bias in crosses with females of the opposite species. This is consistent with the hypothesis that the alleles expressed in the maternal parent cause the female bias, while the Y-linked alleles tend to restore sex ratio toward equality.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Antolin, M. 1992. Sex ratio in structured populations. In: Futyuma D. J. and Antonovics, J. (eds) Oxford Surveys in Evolutionary Biology, vol. 8. Oxford University Press, New York.
Aviles, L. 1993. Interdemic selection and the sex ratio: a social spider perspective. Am Nat, 142, 320–345.
Baker, H G. 1947. Biological flora of the British Isles. Melandrium (Roehling em.) Fries. J Ecol, 35, 271–292.
Baker, H G. 1948. Stages in invasion and replacement demonstrated by species of Melandrium. J Ecol, 36, 96–119.
Carroll, S B, and Mulcahy, D L. 1993. Progeny sex ratios in dioecious Silène latifolia (Caryophyllaceae). Am J Bot, 80, 551–556.
Charlesworth, B. 1991. The evolution of sex chromosomes. Science, 251, 1030–1033.
Charlesworth, B, Coyne, J A, and Barton, N H. 1987. The relative rates of evolution of sex chromosomes and autosomes. Am Nat, 130, 113–146.
Charlesworth, B, Coyne, J A, and Orr, H A. 1993. Meiotic drive and unisexual hybrid sterility: a comment. Genetics, 133, 421–424.
Correns, C. 1928. Bestimmung, Vererbung und Verteilung des geschlechtes bei den hoheren pflanzen. Handb Vererbungsw, 2, 1–138.
Couvet, D, Atlan, A, Belhassen, E, Gliddon, C, Gouyon, P H, and Kjellberg, F. 1991. Coevolution between two symbionts: the case of cytoplasmic male sterility in higher plants. In: Futuyma, D. J. and Antonovics, J. (eds) Oxford Surveys in Evolutionary Biology, pp. 225–249. Oxford University Press, New York.
Coyne, J A, and Orr, H A. 1989a. Patterns of speciation in Drosophila. Evolution, 43, 362–381.
Coyne, J A, and Orr, H A. 1989b. Two rules of speciation. In: Otte, D. and Endler, J., (eds) Speciation and its Consequences. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA.
Coyne, J A, Charlesworth, B, and Orr, H A. 1991. Haldane's rule revisited. Evolution, 45, 1710–1714.
Curtsinger, J W. 1991. X-chromosome segregation distortion in Drosophila. Am Nat, 137, 344–348.
Curtsinger, J W, and Feldman, M W. 1980. Experimental and theoretical analysis of the ‘sex ratio’ polymorphism in Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics, 94, 445–466.
Fisher, R A. 1930. The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Frank, S A. 1989. The evolutionary dynamics of cytoplasmic male sterility. Am Nat, 133, 345–376.
Frank, S A. 1991a. Divergence of meiotic drive suppression systems as an explanation for sex-biased hybrid sterility and inviability. Evolution, 45, 262–267.
Frank, S A. 1991b. Haldane's rule: a defense of the meiotic drive theory. Evolution, 45, 1714–1717.
Fredga, K, Gropp, A, Winking, H, and Frank, F. 1976. Fertile XX- and XY-type females in the wood lemming Myopus schisticolor. Nature, 261, 225–227.
Fredga, K, Gropp, A, Winking, H, and Frank, F. 1977. A hypothesis explaining the exceptional sex ratio in the wood lemming (Myopus schisticolor). Hereditas, 85, 101–104.
Gileva, E. 1987. Meiotic drive in the sex chromosome system of the varying lemming, Dironstonyx torquatus; reproductive performance and its evolutionary significance. Evolution, 36, 601–609.
Godley, E J. 1964. Breeding systems in New Zealand plants. 3. Sex ratios in some natural populations. N Z J Bot, 2, 205–212.
Haldane, J B S. 1922. Sex-ratio and unisexual sterility in hybrid animals. J Genet, 12, 101–109.
Hamilton, W D. 1967. Extraordinary sex ratios. Science, 156, 477–488.
Hickey, W A, and Craig, G B. 1966. Genetic distortion of sex ratio in a mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Genetics, 53, 1177–1196.
Hurst, L D, and Pomiankowski, A. 1991. Causes of sex ratio bias may account for unisexual sterility in hybrids: a new explanation of Haldane's rule and related phenomena. Genetics, 128, 841–858.
Lawrence, C W. 1963. Genetic studies on wild populations of Melandrium. II. Flowering time and plant weight. Heredity, 18, 149–163.
Lloyd, D G. 1973. Sex ratios in sexually dimorphic Umbelli-ferae. Heredity, 31, 239–251.
Lloyd, D G. 1974. Female predominant sex ratios in angiosperme. Heredity, 32, 34–44.
Lovett Doust, J, O'Brien, G, and Lovett Doust, L. 1987. Effect of density on secondary sex characteristics and sex ratio in Silene alba (Caryophyllaceae). Am J Bot, 74, 40–46.
Lyons, E L, Miller, D, and Meagher, T R. 1994. Evolutionary dynamics of sex ratio and gender dimorphism in Silene latifolia. I. Environmental effects. J Hered, (in press).
McNeill, J. 1977. The biology of Canadian weeds. 25. Silene alba (Miller) E.H.L. Krause. Can J Plant Sci, 57, 1103–1114.
Mulcahy, D L. 1967. Optimal sex ratio in Silene alba. Heredity, 22, 411–423.
Van Nigtevecht, G. 1966. Genetic studies in dioecious Melandrium. I. sex-linked and sex-influenced inheritance in Melandrium album and Melandrium dioicum. Genetica, 37, 281–306.
Novitski, E. 1947. Genetic analysis of an anomalous sex ratio condition in Drosophila affinis. Genetics, 32, 526–534.
Nunney, L. 1985. Female-biased sex ratios: individual or group selection?. Evolution, 39, 349–361.
Policansky, D. 1979. Fertility differences as a factor in the maintenance of the ‘sex ratio’, polymorphism is Drosophila pseudoobscura. Am Nat, 108, 75–90.
Pomiankowski, A, and Hurst, L D. 1993. Genomic conflicts underlying Haldane's rule. Genetics, 133, 425–432.
Prentice, H C. 1978. Experimental taxonomy of Silène section Elisanthe (Caryophyllaceae): crossing experiments. Bot J Linn Soc, 77, 203–216.
Prentice, H C. 1984. The sex ratio in a dioecious endemic plant, Silene diclinis. Genetica, 64, 129–133.
Rice, W R. 1989. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution, 43, 223–225.
Rigaud, T, and Juchault, P. 1993. Conflict between feminizing sex ratio distorters and an autosomal masculinizing gene in the terrestrial isopod Armadillidium vulgare Latr. Genetics, 133, 247–252.
Sandler, L, and Novitski, E. 1957. Meiotic drive as an evolutionary force. Am Nat, 61, 105–110.
SAS Institute. 1988. SAS/STAT User's Guide, Release 6.03 Edition. Sas Institute, Cary, NC.
Smith, D A S. 1975. All-female broods in the polymorphic butterfly Danaus chrysippus L. and their ecological significance. Heredity, 34, 363–371.
Sokal, R R, and Rohlf, F J. 1981. Biometry, 2nd edn. W. H. Freeman, New York.
Stalker, H D. 1961. The genetic systems modifying meiotic drive in Drosophila paramelanica. Genetics, 46, 177–202.
Taylor, D R. 1990. Evolutionary consequences of cytoplasmic sex ratio distorters. Evol Ecol, 4, 235.
Taylor, D R. 1992. The Genetic Basis of Sex Ratio Distortion in Silene alba. Ph.D. Thesis, Duke University, Durham, NC.
Taylor, D R. 1994. The genetics basis of sex ratio in Silene alba (= S. latifolia). Genetics, 136, 641–651.
Thompson, G J, and Feldman, M W. 1975. Population genetics of modifiers of meiotic drive. IV. On the evolution of sex ratio distortion. Theor Pop Biol, 8, 202–211.
Trivers, R L, and Hare, H. 1976. Haplodiploidy and the evolution of social insects. Science, 191, 249–263.
Uyenoyama, M K, and Feldman, M. 1978. The genetics of sex ratio distortion by cytoplasmic infection under maternal and contagious transmission: an epidemiological study. Theor Pop Biol, 14, 471–479.
Uyenoyama, M K, and Bengtsson, B O. 1982. Towards a genetic theory for the evolution of sex ratio III. Parental and sibling control of brood investment under partial sib-mating. Theor Pop Biol, 22, 43–68.
Warmke, H E. 1946. Sex determination and sex balance in Melandrium. Am J Bot, 33, 648–660.
Werren, J H. 1980. Sex ratio adaptations to local mate competition in a parasitic wasp. Science, 208, 1157–1159.
Werren, J H. 1983. Sex ratio evolution under local mate competition in a parasitic wasp. Evolution, 37, 116–124.
Werren, J H, Skinner, S W, and Huger, A M. 1986. Male-killing bacteria in a parasitic wasp. Science, 231, 990–992.
Westergaard, M. 1940. Studies on the cytology and sex determination in polyploid forms of Melandrium album. Dansk Botan Arkiv, 10, 1–131.
Westergaard, M. 1958. The mechanism of sex determination in dioecious flowering plants. Adv Genet, 9, 217–281.
Williamson, D L, and Poulson, D F. 1979. Sex ratio organisms (Spiroplasms) of Drosophila. In: Whitcomb, R. F. and Tully, J. G. (eds) The Mycoplasmas, vol. 111, pp. 175–207. Academic Press, New York.
Wilson, D S, and Colwell, R T. 1981. Evolution of sex ratio in structured demes. Evolution, 35, 882–897.
Wood, R J. 1976. Between family variation in sex ratio in the Trinidad (T-30) strain of Aedes aegypti (L.) indicating differences in sensitivity to the meiotic drive gene. Genetica, 46, 345–361.
Wu, C-I. 1983. Virility deficiency and the sex ratio trait in Drosophila pseudoobscura. I. sperm displacement and sexual selection. Genetics, 105, 651–662.
Wu, C-I, and Davies, A W. 1993. Evolution of postmating reproductive isolation: the composite nature of Haldane's Rule and its genetic bases. Am Nat, 142, 187–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, D. Sex ratio in hybrids between Silene alba and Silene dioica: evidence for Y-linked restorers. Heredity 73, 518–526 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1994.150
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1994.150
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Testing the translocation hypothesis and Haldane’s rule in Rumex hastatulus
Protoplasma (2019)
-
Sex determination in dioecious Mercurialis annua and its close diploid and polyploid relatives
Heredity (2015)
-
A sex-chromosome mutation in Silene latifolia
Sexual Plant Reproduction (2011)
-
Evaluating the role of ecological isolation in maintaining the species boundary between Silene dioica and S. latifolia
Plant Ecology (2009)
-
Male gametophyte development and two different DNA classes of pollen grains in Rumex acetosa L., a plant with an XX/XY1Y2 sex chromosome system and a female-biased sex ratio
Sexual Plant Reproduction (2007)