Abstract
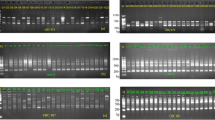
DNA from 57 superior clones was amplified using arbitrary primers in the polymerase chain reaction, in order to assess the genetic variation within Sitka spruce and to investigate if individual clones could be identified. Six out of 30 primers gave reproducible banding patterns. Twenty-four polymorphic bands were scored for the 57 clones studied and all the clones could be identified using a combination of four or more primers. Nei's estimate of similarity was calculated and cluster analysis was used to generate a dendrogram showing considerable variation among the superior trees. Clonally produced material (ramets) could be recognized and mislabelled ramets were identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Adams, W T, and Joly, R J. 1980. Allozyme studies in Loblolly pine seed orchards; clonal variation and frequency of progeny due to self fertilization. Silvae Genet, 29, 1–4.
Alden, J, and Loopstra, C. 1987. Genetic diversity and population structure of Picea glauca on an altitudinal gradient in interior Alaska. Can J Forest Res, 17, 1519–1526.
Bousquet, J, Simon, L, and Lalonde, M. 1990. DNA amplification from vegetative and sexual tissues of trees using polymerase chain reaction. Can J Forest Res, 20, 254–257.
Bucci, G, and Menozzi, P. 1993. Segregation analysis of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers in Picea abies Karst. Mol Ecol, 2, 227–232.
Carlson, J E, Tulsieram, L K, Glaubitz, J C, Luk, V W K, Kauffeldt, C, and Rutledge, R. 1991. Segregation of random amplified DNA markers in F 1 progeny of conifers. Theor Appl Genet, 83, 194–200.
D'Ovidio, R, Tanzarella, O A, and Ponceddu, E. 1990. Rapid and efficient detection of genetic polymorphism in wheat through amplification by polymerase chain reaction. Plant Mol Biol, 15, 169–171.
Forrest, G I. 1994. Biochemical markers in tree improvement programmes. Forestry Abstracts, 55, 123–153.
Graham, J, McNicol, R J, Greig, K, and Van de Ven, W T G. 1994. Identification of red raspberry cultivars and an assessment of their relatedness using fingerprints produced by random primers. J Hort Sci, 69, 123–130.
Hamrick, J L, and Godt, M J W. 1990. Allozyme diversity in plant species. In: Brown, A. H. D., Clegg, M. T., Kahler, A. L. and Weir, B. S. (eds) Plant Population Genetics, Breeding and Genetic Resources, pp. 43–63. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
Harju, A, and Muona, O. 1989. Background pollination in Pinus sylvestris L. seed orchards. Scand J Forest Res, 4, 413–520.
Helentjaris, T, and Burr, B. 1989. Development and Application of Molecular Markers to Problems in Plant Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Karvonen, P, and Savolainen, O. 1992. rdna variation in Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Abstracts of Molecular Biology of Forest Trees, Fifth Workshop of the IUFRO Working Party Molecular Genetics and Cytogenetics, Carcans-Maubuisson, 15–18 June, 1992.
Kremer, A, Moreau, F, Petit, R, Zanetto, A, Bacilieri, R, and Ducousso, A. 1992. Comparison of interspecific variation in European oaks based on allozymes, cpdna, rdna and RAPD'S. Abstracts of International Symposium on Population Genetics and Gene Conservation of Forest Trees, Joint Meeting of IUFRO Working Parties Biochemical Genetics, Population and Ecological Genetics and Subject Group: Provenances, Breeding and Genetic Resources, Carcans-Maubuisson, 24–28 August, 1992.
Lui, Z, and Furnier, G R. 1993. Comparison of allozyme, RFLP, and RAPD markers for revealing genetic variation within and between trembling aspen and bigtooth aspen. Theor Appl Genet, 87, 97–105.
Moreau, E, Kremer, A, Moreau, P, and Petit, R. 1992. Intra- and interspecific variation of random amplified DNA fragments in European oaks. Abstracts of Molecular Biology of Forest Trees, Fifth Workshop of the IUFRO Working Party Molecular Genetics and Cytogenetics, Carcans-Maubuisson, 15–18 June, 1992.
Morgante, M, Vendramin, G G, and Olivieri, A M. 1992. Isolation of molecular markers in Pinus leucodermis Ant. using random amplified polymorphic DNA's. Abstracts of Molecular Biology of Forest Trees, Fifth Workshop of the IUFRO Working Party Molecular Genetics and Cytogenetics, Carcans-Maubuisson, 15–18 June, 1992.
Mosseler, A, Egger, K N, and Hughes, G A. 1992. LOW levels of genetic diversity in red pine confirmed by random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Can J Forest Res, 22, 1332–1337.
Nei, M, and Li, W-H. 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 76, 5269–5273.
Nybom, H, Rogstad, S H, and Schaal, B A. 1990. Genetic variation detected by use of the M13 ‘DNA fingerprint’ probe in Malus, Prunus and Rubus (Rosaceae). Theor Appl Genet, 79, 153–156.
Powell, W, Phillips, M S, McNicol, J W, and Waugh, R. 1991. The use of DNA markers to estimate the extent and nature of genetic variability in Solanum tuberosum cultivars. Ann appl Biol, 118, 423–432.
Rook, D. 1992. Super Sitka for the 90's. Forestry Commission Bulletin, 103, 75 pp.
Skov, E, and Wellendorf, H. 1992. Application of RAPD for high-density genome-mapping and marker-aided selection in Norway spruce. Abstracts of Molecular Biology of Forest Trees, Fifth Workshop of the IUFRO Working Party Molecular Genetics and Cytogenetics, Carcans-Maubuisson, 15–18 June, 1992.
Tulsieram, L K, Glaubitz, J C, Kiss, G, and Carlson, J E. 1992. Single tree genetic linkage mapping in conifers using haploid DNA from megagametophytes. Bio/Technology, 10, 686–690.
Volkaert, H, Hutchison, K W, and Greenwood, M S. 1992. Detection of highly polymorphic DNA sequences and its use in forestry. Abstracts of Molecular Biology of Forest Trees, Fifth Workshop of the IUFRO Working Party Molecular Genetics and Cytogenetics, Carcans-Maubuisson, 15–18 June, 1992.
Wheeler, N C, and Jech, K S. 1992. The use of electrophoretic markers in forest research. New Forests, 6, 311–328.
Wilde, J, Waugh, R, and Powell, W. 1992. Genetic fingerprinting of Theobroma clones using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet, 83, 871–877.
Williams, J G K, Kubelik, A R, Livak, K J, Rafalski, J A, and Tingey, S V. 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res, 18, 6531–6535.
Yeh, F C, and El-Kassaby, Y A. 1980. Enzyme variation in natural populations of Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis). 1. Genetic variation patterns among trees from 10 IUFRO provenances. Can J Forest Res, 10, 214–215.
Yeh, F C, Khalil, M A K, El-Kassaby, Y A, and Trust, D C. 1986. Allozyme variation in Picea mariana from Newfoundland: genetic diversity, population structure, and analysis of differentiation. Can J Forest Res, 16, 713–720.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Scottish Office, Agricultural and Fisheries Department for funding this work, J. E. Cottrell, G. I. Forrest, A. M. Fletcher and D. Rook at the Forestry Authority for guidance and access to their tree plantation, C. Hackett from Scottish Agricultural Statistics Service for statistical guidance, and L. Ross for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van de Ven, W., McNicol, R. The use of RAPD markers for the identification of Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis) clones. Heredity 75, 126–132 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1995.115
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1995.115
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Potential for marker-assisted selection for forest tree breeding: lessons from 20 years of MAS in crops
Tree Genetics & Genomes (2014)
-
Genotypic effects on the variation of wood quality and growth traits in plantation forest made by cutting cultivars of Japanese cedar
Journal of Wood Science (2002)
-
Use of rapd for detecting and identifyingPorphyra (Bangiales, Rhodophyta)
Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology (1998)
-
Genetic Fingerprinting of Nematode-Resistant Clones of Japanese Black Pine (Pinus thunbergiiParl.) Using RAPD Markers
Journal of Forest Research (1998)
-
Optimized conditions for rapd analysis inPinus radiata
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Plant (1998)