Abstract
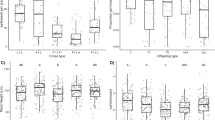
The amphidiploid Trifolium repens L. (2n = 4x = 32) is one of the most agronomically important of the 250–300 species in the genus Trifolium. Seed production is, however, variable and often poor, because of a number of interacting reproductive and climatic factors. Improvement to those characters influencing seed production may be achieved by interspecific hybridization using a closely related species within the genus. One species which has been demonstrated to have a close affinity with T. repens is the annual T. nigrescens (2n = 2x = 16), a prolific flower producer with a less intermittent pattern of flowering than T. repens. Specific cross-combinations of T. repens and T. nigrescens readily produced hybrids without the need of embryo culture. Some F1 hybrids produced large numbers of seed when backcrossed to T. repens. Chromosome counts, isoenzymes and leaf markers confirmed that these were true hybrids. The F1s and BC1s were vigorous plants demonstrating intermediate reproductive characters inherited from the two parental species. This novel approach may be a means of extending the range of heritable variation useful in the breeding and selection of T. repens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Atwood, S S, and Hill, H D. 1940. The regularity of meiosis in microsporocytes of Trifolium repens. Am J Bot, 27, 730–735.
Brewbaker, J L, and Keim, W E. 1953. A fertile interspecific hybrid in Trifolium (4n T. repens L. × 4n T. nigrescens Viv.). Am Nat, 87, 323–326.
Corkill, L. 1971. Leaf markings in white clover. J Hered, 62, 307–310.
Erith, A G. 1924. White Clover-A Monograph. Duckworth and Co., London.
Gibson, P B, Chen, C C, Gillingham, J T, and Barnett, O W. 1971. Interspecific hybridization of Trifolium uniflorum L. Crop Sci, 11, 895–899.
Hill, J, Norris, I B, and Michaelson-Yeates, T P T. 1989. The inheritance of floral characters in white clover (Trifolium repens). Ann Appl Biol, 115, 101–113.
Hollington, P A, Marshall, A H, and Hides, D H. 1989. Effect of seed crop management on potential seed yield of contrasting white clover varieties. II. Seed yield components and potential seed yield. Grass and Forage Sci, 44, 189–193.
Hovin, A W. 1962. Interspecific hybridization between Trifolium repens L. and T. nigrescens Viv. and the analysis of hybrid meiosis. Crop Sci, 2, 251–254.
Keim, W F. 1953. Interspecific hybridization in Trifolium — Utilizing embryo culture techniques. Agron J, 45, 601–606.
Marshall, A H, Hollington, P A, and Hides, D H. 1989. Effect of seed crop management on potential seed yield of contrasting white clover varieties. I. Inflorescence production. Grass and Forage Sci, 44, 181–188.
Marshall, A H. 1994. Seasonal variation in the seed yield components of white clover. Plant, Varieties and Seeds, 7, 97–105.
Michaelson-Yeates, T P T. 1986. Phosphoglucoisomerase variation in Trifolium repens. Genetica, 70, 53–58.
Thomas, R G. 1981. Effect of defoliation on flower initiation in white clover in summer. Grass and Forage Sci, 36, 121–125.
Trimble, J P. 1951. Interspecific Hybridization Studies in the Genus Trifolium. M.S. Thesis, Pennsylvania State College.
Williams, E. 1978. A hybrid between Trifolium repens and T. ambiguum obtained with the aid of embryo culture. N Z J Bot, 16, 499–506.
Williams, R D. 1925. Self and cross-sterility in white clover. Bull Welsh Pl Breed Station, Series H, 12, 209–220.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marshall, A., Michaelson-Yeates, T., Aluka, P. et al. Reproductive characters of interspecific hybrids between Trifolium repens L. and T. nigrescens Viv.. Heredity 74, 136–145 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1995.20
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1995.20
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pedigree analysis of pre-breeding efforts in Trifolium spp. germplasm in New Zealand
BMC Genetics (2020)
-
Genetic diversity in white clover and its progenitors as revealed by DNA fingerprinting
Biologia plantarum (2012)
-
Genetic similarity among Trifolium species based on isozyme banding pattern
Plant Systematics and Evolution (2008)