Abstract
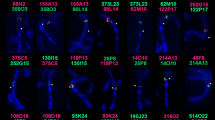
We investigated the possible application of RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) analysis to the study of the systematic relationships of five cervid taxa. Amplifications with eight different primers gave reproducible electrophoretic patterns which could be regarded as a data-set consisting of monomorphic and polymorphic characters. Some of these characters are species- and subspecies-specific. Band-sharing analysis and numerical taxonomy methods allowed us to generate a phenetic tree. Our results point out new possible systematic considerations within the examined taxa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Bandi, C, La Rosa, G, Bardin, M G, Damiani, G, Comincini, S, Tracsiotti, L, and Pozio, E. 1995. Random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting of eight taxa of Trichinella and their comparison with allozyme analysis. Parasitology, 110, 401–407.
Baruffi, L, Damiani, G, Guglielmino, C R, Bandi, C, Malacrida, A R, and Gasperi, G. 1995. Polymorphism within and between populations of Ceratitis capitata: comparison between RAPD and multilocus enzyme electrophoresis data. Heredity, 74, 425–437.
Bogenberger, J M, Neitzel, H, and Fittler, F. 1987. A highly repetitive DNA component common to all Cervidae: its organisation and chromosomal distribution during evolution. Chromosoma, 95, 154–161.
Brooke, V. 1878. On the classification of the Cervidae, with a synopsis of the existing species. Proc Zool Soc London, 1878, 883–928.
Castiglione, S, Wang, G, Damiani, G, Bandi, C, Bisoffi, S, and Sala, F. 1993. RAPD fingerprinting identification for taxonomic studies of elite popular (Populus spp.) clones. Theor Appl Genet, 87, 54–59.
Chalmers, K J, Waugh, K, Sprent, J I, Simons, A J, and Powell, W. 1992. Detection of genetic variation between and within populations of Gliricidia sepium and G. maculata using RAPD markers. Heredity, 69, 465–472.
Clark, A G, and Lanigan, C M S. 1993. Prospects for estimating nucleotide divergence with RAPDs. Mol Biol Evol, 10, 1096–1111.
Cronin, M A. 1991. Mitochondrial-DNA phylogeny of deer (Cervidae). J Mammal, 72, 553–556.
Demeke, T, Adams, R P, and Chibbar, R. 1992. Potential taxonomic use of Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD): a case study in Brassica. Theor Appl Gen, 84, 990–994.
Emerson, B C, and Tate, M L. 1993. Genetic analysis of evolutionary relationships among deer (Subfamily Cervinae). J Hered, 84, 226–273.
Fani, R, Bandi, C, Bardin, M G, Comincini, S, Damiani, G, Grifoni, A, and Bazzicalupo, M. 1993. RAPD fingerprinting is useful for identification of Azospirillum strains. Microb Release, 1, 217–221.
Felstenstein, J. 1993. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) Version 3.5c. Software package distributed by the author. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Fontana, F, and Rubini, M. 1990. Chromosomal evolution in Cervidae. Biosystems, 24, 157–174.
Gilbert, D A, Lehman, N, O'Brien, S J, and Wayne, R K. 1990. Genetic fingerprinting reflects population differentiation in the California Channel Island fox. Nature, 344, 764–767.
Groves, C P, and Grubb, P. 1987. Relationships of living deer. In: Wemmet, C. M. (ed.) Biology and Management of the Cervidae, pp. 21–59. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C.
Gwakisa, P S, Kemp, S J, and Teale, T. 1994. Characterisation of Zebu cattle breeds in Tanzania using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Anim Genet, 25, 89–94.
Hadrys, H, Balick, M, and Schierwater, B. 1992. Applications of Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in molecular ecology. Mol Ecol, 1, 55–63.
Harrington, R. 1985. Evolution and distribution of the Cervidae. In: Fennessy, F. F. and Drew, K. R. (eds) The Biology of Deer Production, vol. 22, pp. 3–11. Royal Society New Zealand Bulletin.
Kaukas, A, Dias-Neto, E, Simpson, A J, Southgate, V R, and Rollinson, V. 1994. A phylogenetic analysis of Schistosoma haematobium group species based on randomly amplified polymorphic DNA. Int J Parasitol, 24, 285–299.
Lynch, M. 1990. The similarity index and DNA fingerprinting. Mol Biol Evol, 7, 478–484.
Lynch, M, and Milligan, R. 1994. Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Mol Ecol, 3, 91–99.
Miyamoto, M M, Kraus, F, and Ryder, O A. 1990. Phylogeny and evolution of antlered deer determined from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad USA, 87, 6127–6131.
Neitzel, H. 1987. Chromosome evolution in Cervidae: karyotypic and molecular aspects. In: Obe, R. and Basler, T. (eds) Cytogenetics, pp. 90–112. Springer, Berlin.
Rothuizen, J, and Van Wolferen, R. 1994. Randomly amplified DNA polymorphisms in dogs are reproducible and display Mendelian transmission. Anim Genet, 25, 13–18.
Rubini, M, Negri, E, and Fontana, F. 1990. Standard karyotype and chromosomal evolution of the fallow deer (Dama dama L.). Cytobios, 155, 155–161.
Sambrook, J, Fritsch, E F, and Maniatis, T. 1989. Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Scherthan, H, Arnason, U, and Lima-De-Faria, A. 1987. The chromosome field theory tested in muntjac species by DNA cloning and hybridization. Hereditas, 107, 175–184.
Sneath, P H A, and Sokal, H R. 1973. Numerical Taxonomy. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco.
Tibayrenc, M, Neubauer, K, Barnabé, C, Guerrini, F, Skarecky, D, and Ayala, F J. 1993. Genetic characterization of six parasitic protozoa: Parity between random-primer DNA typing and multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90, 1335–1339.
Wang, Z, and Du, R. 1988. Karyotypes and Chromosomal Evolution in Deer. Scientific Publishing House, Beijing.
Welsh, J, and McClelland, M. 1990. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucl Acids Res, 18, 7213–7218.
Wessmann, M, and Gripenberger, U. 1993. Restriction endonuclease staining profiles in the C-heterochromatin of Cervidae. I. The autosome. Hereditas, 118, 243–249.
Williams, J G K, Kubelik, A R, Livak, K J, Rafalki, J A, and Tingey, S V. 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res, 18, 6531–6535.
Wurster, D H, and Benirschke, K. 1970. Indian muntjac, Muntiacus muntjac: a deer with a low diploid chromosome number. Science, 168, 1364–1366.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comincini, S., Sironi, M., Bandi, C. et al. RAPD analysis of systematic relationships among the Cervidae. Heredity 76, 215–221 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1996.34
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1996.34
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular Phylogeny of Deer (Cervidae: Artiodactyla)
Russian Journal of Genetics (2005)
-
Phylogenetic relationships among deer in China derived from mitochondrial DNA cytochromeb sequences
Acta Theriologica (2003)
-
Evaluation of random amplified polymorphic DNA for species identification and phylogenetic analysis inStylosanthes (Fabaceae)
Plant Systematics and Evolution (1998)
-
Taxonomic relationships in East AsianVicia species with unijugate leaves based on random amplified polymorphic DNA markers
Journal of Plant Biology (1998)
-
Variability of the bushcricket Ephippiger ephippiger: RAPDs and song races
Heredity (1997)