Abstract
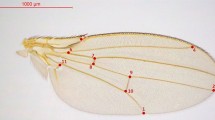
Plasticity in wing characters was investigated in lines selected for long and short wing length and for long and short thorax length in Drosophila melanogaster. Selection lines were reared at 20°C and at 25°C. All lines were raised across a temperature range from 17.5°C to 27.5°C after several generations of directional selection. We tested whether correlated responses in wing cell size and cell number and in plasticity occurred as a result of selection on wing size or thorax size. A difference in plasticity in the lines was observed at different selection temperatures. Selection at 25°C resulted only in a change in mean values, whereas selection at 20°C led to some correlated responses in plasticity. Different results might have been obtained if more replicates of the selection lines had been started from the same population. The results show that mean size at a temperature and plasticity across temperatures are at least partly determined by different genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Bradshaw, A D. 1965. Evolutionary significance of pheno-typic plasticity in plants. Adv Genet, 13, 115–155.
Cavicchi, S, Guerra, D, Giorgio, G, and Pezzoli, C. 1985. Temperature-related divergence in experimental populations of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Genetic and developmental basis of wing size and shape variation. Genetics, 109, 665–689.
De Jong, G. 1995. Phenotypic plasticity as a product of selection in a variable environment. Am Nat, 145, 493–512.
Dobzhansky, T H. 1929. The influence of the quantity and quality of the chromosomal material on the size of the cells in Drosophila melanogaster. Arch Entwicklungsmech Organ, 115, 363–379.
Falconer, D S. 1952. The problem of environment and selection. Am Nat, 86, 293–298.
Falconer, D S. 1989. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 3rd edn. Longman, New York.
Falconer, D S. 1990. Selection in different environments: effects on environmental sensitivity (reaction norm) and on mean performance. Genet Res, 56, 57–70.
Gromko, M H. 1995. Unpredictability of correlated response to selection: pleiotropy and sampling interact. Evolution, 49, 685–693.
Jinks, J L, and Connolly, V. 1973. Selection for specific and general response to environmental differences. Heredity, 30, 33–40.
Mittler, S, and Bennett, J. 1962. A simple food medium that requires no live yeast with a minimum of variables. Drosoph Inf Serv, 36, 131–132.
Partridge, L, Barry, B, Fowler, K, and French, V. 1994. Evolution and development of body size and cell size in Drosophila melanogaster in response to temperature. Evolution, 48, 1269–1276.
Reeve, E C R. 1961. A note on non-random mating in progeny tests. Genet Res, 2, 195–203.
Robertson, F W. 1959a. Studies in quantitative inheritance XII. Cell size and number in relation to genetic and environmental variation of body size in Drosophila. Genetics, 44, 869–896.
Robertson, F W. 1959b. Studies in quantitative inheritance XIII. Interrelations between genetic behavior and development in the cellular constitution of the Drosophila wing. Genetics, 44, 1113–1130.
Robertson, F W, and Reeve, E C R. 1952. Studies in quantitative inheritance. I. The effects of selection of wing and thorax length in Drosophila melanogaster. J Genet, 50, 414–448.
Scheiner, S M. 1993. Plasticity as a selectable trait: reply to Via. Am Nat, 142, 371–373.
Scheiner, S M, and Lyman, R F. 1989. The genetics of phenotypic plasticity. I. Heritability. J Evol Biol, 2, 95–107.
Scheiner, S M, and Lyman, R F. 1991. The genetics of phenotypic plasticity. II. Response to selection. J Evol Biol, 4, 23–50.
Schlichting, C D. 1993. Control of phenotypic plasticity via regulatory genes. Am Nat, 142, 366–370.
Sokal, R R, and Rohlf, F J. 1981. Biometry, 2nd edn. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco.
Via, S. 1987. Genetic constraints on the evolution of phenotypic plasticity. In: Loeschcke, V. (ed.) Genetic Constraints on Adaptive Evolution, pp. 47–71. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Via, S. 1993. Adaptive phenotypic plasticity: target or by-product of selection in a variable environment? Am Nat, 142, 352–365.
Via, S, and Lande, R. 1985. Genotype-environment interaction and the evolution of phenotypic plasticity. Evolution, 39, 505–522.
Via, S, Gomulkiewicz, R, De Jong, G, Scheiner, S M, Schlichting, C D, and Van Tienderen, P. 1995. Adaptive phenotypic plasticity: consensus and controversy. Trends Ecol Evol, 10, 212–217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noach, E., De Jong, G. & Scharloo, W. Phenotypic plasticity of wings in selection lines of Drosophila melanogaster. Heredity 79, 1–9 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1997.116
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1997.116
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Starvation-Induced Dietary Behaviour in Drosophila melanogaster Larvae and Adults
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Cellular basis of morphological variation and temperature-related plasticity in Drosophila melanogaster strains with divergent wing shapes
Genetica (2014)
-
Achieving temperature-size changes in a unicellular organism
The ISME Journal (2013)