Abstract
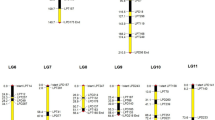
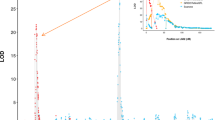
In order to detect the linkage disequilibrium existing between alleles at a marker locus and alleles of a linked quantitative trait locus (QTL), a least squares interval mapping approach using multiple regression on marker data has been developed. It allows inclusion in the model of the parameters describing the experimental and environmental situation, so that the QTL × environment effects can be tested. The method can also be applied using any general statistical package to data for which the usual normal distribution assumption does not hold, and where the use of weighted approaches is therefore required. A method to cope with the frequent problem in biological experiments of missing data was also used. The analysis was performed on data concerning two components of maize pollen competitive ability, obtained from an experiment over 2 years. The method, in comparison with the traditional single marker approach, has been shown to be more powerful in detecting QTLs and more precise in determining their map position. The analysis has identified QTLs expressed across years, putative QTLs with major effects and QTLs accounting for genotype × environment interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Beavis, W D, Smith, O S, Grant, D, and Fincher, R. 1994. Identification of quantitative trait loci using a small sample of topcrossed and F4 progeny from maize. Crop Sci, 34, 882–896.
Bubeck, D M, Goodman, M M, Beavis, W D, and Grant, D. 1993. Quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to grey leaf spot in maize. Crop Sci, 33, 838–847.
Burr, B, and Burr, F A. 1991. Recombinant inbreds for molecular mapping in maize: theoretical and practical considerations. Trends Genet, 7, 55–60.
Burr, B, Burr, F A, Thompson, K H, Albertson, M C, and Stuber, C W. 1988. Gene mapping with recombinant inbreds in maize. Genetics, 118, 519–526.
Edwards, M D, Stuber, C W, and Wendel, J F. 1987. Molecular-marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative-trait loci in maize. I. Numbers, genomic distribution and types of gene action. Genetics, 116, 113–125.
Genstat 5 Committee, 1993. Genstat 5 Release 3 Reference Manual. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Grizzle, J E, Starmer, C F, and Koch, G G. 1969. Analysis of categorical data by linear models. Biometrics, 25, 489–504.
Guffy, R D, Stuber, C W, and Edwards, M D. 1989. Dissecting and enhancing heterosis in corn using molecular markers. In: Proc 25th Illinois Corn Breeders School, pp. 99–120. Champaign, IL.
Haldane, J B S, and Waddington, C H. 1931. Inbreeding and linkage. Genetics, 16, 357–374.
Haley, C S, and Knott, S A. 1992. A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity, 69, 315–324.
Hayes, P M, Liu, B H, Knapp, S J, Chen, F, Jones, B, and Blake, T. et al. 1993. Quantitative trait locus effects and environmental interaction in a sample of North American barley germplasm. Theor Appl Genet, 87, 392–401.
Hochberg, Y, and Tamhane, A C. 1987. Multiple Comparison Procedures. Wiley, New York.
Jansen, R C. 1993. Interval mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Genetics, 135, 205–211.
Jansen, R C. 1994. Controlling the type I and type II errors in mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics, 138, 871–881.
Jansen, R C, and Stam, P. 1994. High resolution of quantitative traits into multiple loci via interval mapping. Genetics, 136, 1447–1455.
Jansen, R C, Van Ooijen, J W, Stam, P, Lister, C, and Dean, C. 1995. Genotype-by-environment interaction in genetic mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet, 91, 33–37.
Knapp, S J, Bridges, W C, and Birked, D. 1990. Mapping quantitative trait loci using molecular marker linkage maps. Theor Appl Genet, 79, 583–592.
Koch, G G, Landis, J R, Freeman, J L, and Freeman, D H, Jr. 1977. A general methodology for the analysis of experiments with repeated measurement of categorical data. Biometrics, 33, 133–158.
Koester, R P, Sisco, P H, and Stuber, C W. 1993. Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling days to flowering and plant height in two near isogenic lines of maize. Crop Sci, 33, 1209–1216.
Lander, E S, and Bostein, D. 1989. Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics, 121, 185–199.
Martinez, O, and Curnow, R N. 1994. Missing markers when estimating quantitative trait loci using regression mapping. Heredity, 73, 198–206.
Paterson, A H, Damon, S, Hewitt, J D, Zamir, D, Rabinowitch, H D, and Lincoln, S E. et al. 1991. Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits in tomato: comparison across species, generations, and environments. Genetics, 127, 181–197.
Paterson, A H, Lander, E S, Hewitt, J D, Peterson, S, Lincoln, S E, and Tanksley, S D. 1988. Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature, 335, 721–726.
Rodolphe, F, and Lefort, M. 1993. A multi-marker model for detecting chromosomal segments displaying QTL activity. Genetics, 134, 1277–1288.
Sari-Gorla, M, Pé, M E, Mulcahy, D L, and Ottaviano, E. 1992. Genetic dissection of pollen competitive ability in maize. Heredity, 69, 423–430.
Sari-Gorla, M, Binelli, G, Pé, M E, and Villa, M. 1995. Detection of genetic factors controlling pollen-style interaction in maize. Heredity, 74, 62–69.
Schön, C C, Melchinger, A E, Boppenmaier, J, Brunklaus-Jung, E, Herrmann, R G, and Seitzer, J F. 1994. RFLP mapping in maize: quantitative trait loci affecting testcross performance of elite European flint lines. Crop Sci, 34, 378–389.
Simpson, S P. 1989. Detection of linkage between quantitative trait loci and restriction fragment length polymorphisms using inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet, 77, 815–819.
Soller, M, and Beckman, J S. 1983. Genetic polymorphism in varietal identification and genetic improvement. Theor Appl Genet, 67, 25–33.
Soller, M, Genizi, A, and Brody, T. 1976. On the power of experimental designs for the detection of linkage between marker loci and quantitative loci in crosses between inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet, 47, 35–39.
Stuber, C W, Lincoln, S E, Wolff, D W, Helentjaris, T, and Lander, E S. 1992. Identification of genetic factors contributing to heterosis in a hybrid from two elite maize inbred lines using molecular markers. Genetics, 132, 823–839.
Weisberg, S. 1985. Applied Linear Regression, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York.
Weller, J I, Soller, M, and Brody, T. 1988. Linkage analysis of quantitative traits in an interspecific cross of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum × Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium) by means of genetic markers. Genetics, 118, 329–339.
Zehr, B E, Dudley, J W, Chojecki, M A, Maroof, S, and Mowers, R P. 1992. Use of RFLP markers to search for alleles in a maize population for improvement of an elite hybrid. Theor Appl Genet, 83, 903–911.
Zeng, Z-B. 1993. Theoretical basis of separation of multiple linked gene effects on mapping quantitative trait loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90, 10972–10976.
Zeng, Z-B. 1994. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics, 136, 1457–1468.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sari-Gorla, M., Calinski, T., Kaczmarek, Z. et al. Detection of QTL × environment interaction in maize by a least squares interval mapping method. Heredity 78, 146–157 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1997.22
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1997.22