Abstract
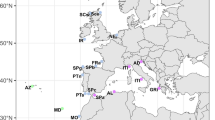
Eleven enzymes coded by 15 loci (ADH*, SOD*, SDH*, LDH-1*, LDH-2*, ME-1*, ME-2*, GPI-1*, GPI-2*, IDH*, MDH-1*, MDH-2*, PGM*, AAT* and CK*) were studied using electrophoretic methods in order to characterize stocks of sardines from the western Mediterranean Sea. The results showed differentiated groups distributed throughout the area studied. They did not form a panmictic population, but they existed as semi-independent, although not completely isolated, breeding units with an estimation of migration of Nem = 3.1 (number of migrants per generation). In the LDH-1 system a north-south cline was detected. We have also detected a discontinuity between the Alboran and the rest of the Mediterranean populations sampled at the enzymatic level. This result confirms the action of the Almeria–Oran front as a barrier that produces discontinuities as detected in other marine species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Alemany, F, and Alvarez, F. 1993. Growth differences among sardine (Sardina pilchardus Walb.) populations in Western Mediterranean. Sci Mar, 57, 229–234.
Allendorf, F W, Mitchell, N, Ryman, N, and Stähl, G. 1977. Isozyme loci in brown trout (Salmo trutta L.): detection and interpretation from population data. Hereditas, 86, 179–190.
Altukhov, Y P, and Salmenkova, E A. 1987. Stock transfer relative to natural organization, management and conservation of fish populations. In: Ryman, N. and Utter, F. (eds) Population Genetics and Fishery Management, pp. 333–344. University of Washington Press, Seattle.
Carvalho, G R, and Hauser, L. 1994. Molecular genetics and the stock concept in fisheries. Rev Fish Biol Fish, 4, 326–350.
Chabanaud, P. 1926. Sur les clupeides du genre Sardina et de divers genres voisins. Bull Soc Zool France, 51, 8–16.
Clayton, J W, and Tetriak, D N. 1972. Amine-citrate buffers for pH control in starch gel electrophoresis. J Fish Res Board Can, 29, 1169–1172.
Felsenstein, J. 1993. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package). Version 3.5c. Univ. of Washington, Seattle.
Furnestin, J. 1952. Biologie de clupeides mediterranees. Journées d'Etudes du Laboratoire Arago (Suppl. No. 3 a Vie et Milieu), 2, 96–116.
Gyllensten, U. 1985. The genetic structure of fish: differences in the intraspecific distribution of biochemical genetic variation between marine, anadromous, and freshwater species. J Fish Biol, 26, 691–699.
Harris, H, and Hopkinson, D A. 1976. Handbook of Enzyme Electrophoresis in Human Genetics. North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Jamieson, A. 1973. Genetic ‘tags’ for marine fish stocks. In: Hardin, J. F. R. (ed.) Sea Fisheries Research, pp. 91–99. Elek Science, London.
Laskaridis, K. 1948. Study of the biology of sardine (Clupea pilchardus Walb.) in Greek waters. Prakt Hell Hydrobiol Fish Bull, 85, 561–568.
Lee, J Y. 1962. Sardines de l'Atlantique et sardines de la Mediterranée. Différences morphologiques, biologiques et sérologiques. Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer. Council Meeting. Comité de la Sardine. No. 14, 1–5.
Nei, M. 1972. Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat, 106, 283–292.
Powers, D A, Lauerman, T, Crawford, D, Smith, M, Gonzalez-Villasenor, I, and Dimichele, L. 1991. The evolutionary significance of genetic variation at enzyme synthesizing loci in the teleost Fundulus heteroclitus. J Fish Biol, 39 (Suppl. A), 169–184.
Quesada, H, Zapata, C, and Alvarez, G. 1995a. A multilocus allozyme discontinuity in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: the interaction of ecological and life-history factors. Mar Ecol Progr Ser, 116, 99–115.
Quesada, H, Beynon, C M, and Skibinski, D O F. 1995b. A mitochondrial DNA discontinuity in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk: Pleistocene vicariance biogeography and secondary intergradation. Mol Biol Evol, 12, 521–524.
Ridgway, G J, Sherburne, S W, and Lewis, R D. 1970. Polymorphism in the esterases of Atlantic herring. Trans Am Fish Soc, 99, 147–151.
Rodriguez, J, Garcia, A, and Rodriguez, V. 1979. Zooplanktonic communities of the divergence zone in the northwestern Alboran Sea. Mar Ecol, 3, 133–142.
Ryman, N. 1983. Patterns of distribution of biochemical genetic variation in salmonids: differences between species. Aquaculture, 33, 1–21.
Saavedra, C, Zapata, C, Guerra, A, and Alvarez, G. 1993. Allozyme variation in European populations of the oyster Ostrea edulis. Mar Biol, 115, 85–95.
Shaklee, J B. 1983. The utilization of isozymes as gene markers in fisheries management and conservation. Isozymes: Cum Top Biol Med Res, 11, 213–247.
Shaklee, J B, Phelps, S R, and Salini, J. 1990. Analysis of fish stock structure and mixed-stock fisheries by electrophoretic characterization of allelic isozymes. In: Whitmore, D. H. (ed.) Electrophoretic and Isoelectric Focusing Techniques in Fisheries Management pp. 173–196. CRC Press, Boca Raton FL.
Skaala, O, Dahle, G, Jørstad, K, and Nævdal, G. 1990. Interactions between natural and farmed fish populations: information from genetic markers. J Fish Biol, 36, 449–460.
Skrivanic, A, and Zavodnik, D. 1973. Migration of the sardine (Sardina pilchardus) in relation to hydrographical conditions of the Adriatic Sea. Neth J Sea Res, 7, 7–18.
Smith, P J. 1986. Genetic similarity between samples of the orange roughly Hoplostethus atlanticus from the Tasman Sea, south-west Pacific Ocean and north-east Atlantic Ocean. Mar Biol, 91, 173–180.
Smith, P J, Jamieson, A, and Birley, A J. 1990. Electrophoretic studies and stock concept in marine teleosts. J Cons int Explor Mer, 47, 231–245.
Sokal, R R, and Rohlf, F J. 1981. Biometry, 2nd edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York.
Spanakis, E, Tsimenides, N, and Zouros, E. 1989. Genetic differences between populations of sardine, Sardina pilchardus, and anchovy, Engraulis encrasicolus, in the Aegean and Ionian Seas. J Fish Biol, 35, 417–437.
Stähl, G. 1987. Genetic population structure of Atlantic Salmon. In: Ryman, N. and Utter, F. (eds) Population Genetics and Fishery Management, pp. 121–140. University of Washington Press, Seattle.
Svetovidov, A N. 1964. Rydy Tchernogo More. Zoologicheskii Institut Akademii Nauk SSSR. Moscow-Leningrad.
Swofford, D L, and Selander, R B. 1989. BIOSYS-1. A computer program for the analysis of allelic variation in population genetics and biochemical systematics. Release 1.7. University of Illinois, Urbana, IL.
Tintoré, J, La Violette, P E, Blade, I, and Cruzado, G. 1988. A study of an intense density front in the eastern Alboran Sea: the Almería-Oran front. J Phys Oceanogr, 18, 1384–1397.
Utter, F M. 1991. Biochemical genetics and fishery management: an historical perspective. J Fish Biol, 39 (Suppl. A), 1–20.
Ward, R D, Woodwark, M, and Skibinski, D O F. 1994. A comparison of genetic diversity levels in marine, freshwater, and anadromous fishes. J Fish Biol, 44, 213–232.
Weir, B S. 1990. Genetic Data Analysis. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
Wilmot, R L, and Burger, C V. 1985. Genetic differences among populations of Alaskan sockeye salmon. Trans Am Fish Soc, 114, 236–243.
Wolf, V, Engel, W, and Faust, J. 1970. Zum Mechanismus der Diploidisierung in der Wirbeltierevolution: Koexistenz von tetrasomen und disomen Genloci der Isocitrat-dehydrogenasen bei der Regenbogenforelle (Salmo irideus). Humangenetik, 9, 150–156.
Wright, S. 1951. The genetical structure of populations. Ann Eugen, 15, 323–354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramon, M., Castro, J. Genetic variation in natural stocks of Sardina pilchardus (sardines) from the western Mediterranean Sea. Heredity 78, 520–528 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1997.81
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1997.81
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The current knowledge status of the genetic population structure of the European sardine (Sardina pilchardus): uncertainties to be solved for an appropriate fishery management
Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries (2022)
-
First global approach: morphological and biological variability in a genetically homogeneous population of the European pilchard, Sardina pilchardus (Walbaum, 1792) in the North Atlantic coast
Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries (2012)
-
Integrating fish and parasite data as a holistic solution for identifying the elusive stock structure of Pacific sardines (Sardinops sagax)
Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries (2012)
-
Identification of subpopulations in pelagic marine fish species using amino acid composition
Hydrobiologia (2011)
-
Genetic population structure of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) off Morocco detected with intron polymorphism (EPIC-PCR)
Marine Biology (2007)